Amphiregulin is an essential mediator of estrogen receptor alpha function in mammary gland development
- PMID: 17369357
- PMCID: PMC1838509
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0611647104
Amphiregulin is an essential mediator of estrogen receptor alpha function in mammary gland development
Abstract
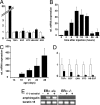
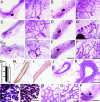
Most mammary gland development occurs after birth under the control of systemic hormones. Estrogens induce mammary epithelial cell proliferation during puberty via epithelial estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) by a paracrine mechanism. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling has long been implicated downstream of ERalpha signaling, and several EGFR ligands have been described as estrogen-target genes in tumor cell lines. Here, we show that amphiregulin is the unique EGF family member to be transcriptionally induced by estrogen in the mammary glands of puberal mice at a time of exponential expansion of the ductal system. In fact, we find that estrogens induce amphiregulin through the ERalpha and require amphiregulin to induce proliferation of the mammary epithelium. Like ERalpha, amphiregulin is required in the epithelium of puberal mice for epithelial proliferation, terminal end buds formation, and ductal elongation. Subsequent stages, such as side-branching and alveologenesis, are not affected. When amphiregulin(-/-) mammary epithelial cells are in close vicinity to wild-type cells, they proliferate and contribute to all cell compartments of the ductal outgrowth. Thus, amphiregulin is an important paracrine mediator of estrogen function specifically required for puberty-induced ductal elongation, but not for any earlier or later developmental stages.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Amphiregulin: role in mammary gland development and breast cancer.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008 Jun;13(2):159-69. doi: 10.1007/s10911-008-9075-7. Epub 2008 Apr 9. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008. PMID: 18398673 Review.
-
Mammary ductal morphogenesis requires paracrine activation of stromal EGFR via ADAM17-dependent shedding of epithelial amphiregulin.Development. 2005 Sep;132(17):3923-33. doi: 10.1242/dev.01966. Epub 2005 Aug 3. Development. 2005. PMID: 16079154 Free PMC article.
-
2-methoxyestradiol induces mammary gland differentiation through amphiregulin-epithelial growth factor receptor-mediated signaling: molecular distinctions from the mammary gland of pregnant mice.Endocrinology. 2007 Mar;148(3):1266-77. doi: 10.1210/en.2006-0964. Epub 2006 Dec 7. Endocrinology. 2007. PMID: 17158205
-
Estrogen receptor-alpha expression in the mammary epithelium is required for ductal and alveolar morphogenesis in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Sep 11;104(37):14718-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706933104. Epub 2007 Sep 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17785410 Free PMC article.
-
The ADAM17-amphiregulin-EGFR axis in mammary development and cancer.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008 Jun;13(2):181-94. doi: 10.1007/s10911-008-9084-6. Epub 2008 May 10. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008. PMID: 18470483 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Establishing conditions for the generation and maintenance of estrogen receptor-positive organoid models of breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2024 Mar 29;26(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13058-024-01798-6. Breast Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38553763 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell and spatial analyses reveal a tradeoff between murine mammary proliferation and lineage programs associated with endocrine cues.Cell Rep. 2023 Oct 31;42(10):113293. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113293. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37858468 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct Requirements for Adaptor Proteins NCK1 and NCK2 in Mammary Gland Development.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2023 Jul 21;28(1):19. doi: 10.1007/s10911-023-09541-1. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2023. PMID: 37479911 Free PMC article.
-
Cell type and stage specific transcriptional, chromatin and cell-cell communication landscapes in the mammary gland.Heliyon. 2023 Jun 30;9(7):e17842. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17842. eCollection 2023 Jul. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37456014 Free PMC article.
-
ERBB Receptors and Their Ligands in the Developing Mammary Glands of Different Species: Fifteen Characters in Search of an Author.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2023 May 23;28(1):10. doi: 10.1007/s10911-023-09538-w. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2023. PMID: 37219601 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

