Strong association of de novo copy number mutations with autism
- PMID: 17363630
- PMCID: PMC2993504
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1138659
Strong association of de novo copy number mutations with autism
Abstract
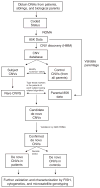
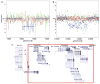
We tested the hypothesis that de novo copy number variation (CNV) is associated with autism spectrum disorders (ASDs). We performed comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) on the genomic DNA of patients and unaffected subjects to detect copy number variants not present in their respective parents. Candidate genomic regions were validated by higher-resolution CGH, paternity testing, cytogenetics, fluorescence in situ hybridization, and microsatellite genotyping. Confirmed de novo CNVs were significantly associated with autism (P = 0.0005). Such CNVs were identified in 12 out of 118 (10%) of patients with sporadic autism, in 2 out of 77 (3%) of patients with an affected first-degree relative, and in 2 out of 196 (1%) of controls. Most de novo CNVs were smaller than microscopic resolution. Affected genomic regions were highly heterogeneous and included mutations of single genes. These findings establish de novo germline mutation as a more significant risk factor for ASD than previously recognized.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Copy number variations associated with idiopathic autism identified by whole-genome microarray-based comparative genomic hybridization.Psychiatr Genet. 2009 Aug;19(4):177-85. doi: 10.1097/YPG.0b013e32832bdafa. Psychiatr Genet. 2009. PMID: 19407672
-
[Genomic abnormalities in children with mental retardation and autism: the use of comparative genomic hybridization in situ (HRCGH) and molecular karyotyping with DNA-microchips (array CGH)].Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2013;113(8):46-9. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2013. PMID: 24077551 Russian.
-
Novel submicroscopic chromosomal abnormalities detected in autism spectrum disorder.Biol Psychiatry. 2008 Jun 15;63(12):1111-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.01.009. Epub 2008 Mar 28. Biol Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 18374305 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent rearrangements in synaptic and neurodevelopmental genes and shared biologic pathways in schizophrenia, autism, and mental retardation.Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009 Sep;66(9):947-56. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.80. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19736351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Copy number variations and clinical cytogenetic diagnosis of constitutional disorders.Nat Genet. 2007 Jul;39(7 Suppl):S48-54. doi: 10.1038/ng2092. Nat Genet. 2007. PMID: 17597782 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of genetic variants with autism spectrum disorder in Japanese children revealed by targeted sequencing.Front Genet. 2024 Aug 30;15:1352480. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1352480. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39280100 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal environmental risk factors for autism spectrum disorder and their potential mechanisms.BMC Med. 2024 Sep 16;22(1):393. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03617-3. BMC Med. 2024. PMID: 39278907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atopic Dermatitis and Autism Spectrum Disorders: Common Role of Environmental and Clinical Co-Factors in the Onset and Severity of Their Clinical Course.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 16;25(16):8936. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168936. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Copy-number variants differ in frequency across genetic ancestry groups.HGG Adv. 2024 Oct 10;5(4):100340. doi: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2024.100340. Epub 2024 Aug 12. HGG Adv. 2024. PMID: 39138864 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome sequencing identifies novel genes for autism in Chinese trios.Sci China Life Sci. 2024 Nov;67(11):2368-2381. doi: 10.1007/s11427-023-2564-8. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Sci China Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39126614
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

