Structures of T Cell immunoglobulin mucin receptors 1 and 2 reveal mechanisms for regulation of immune responses by the TIM receptor family
- PMID: 17363299
- PMCID: PMC7111020
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.01.014
Structures of T Cell immunoglobulin mucin receptors 1 and 2 reveal mechanisms for regulation of immune responses by the TIM receptor family
Abstract
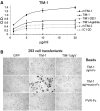
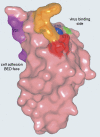
The T cell immunoglobulin mucin (TIM) receptors are involved in the regulation of immune responses, autoimmunity, and allergy. Structures of the N-terminal ligand binding domain of the murine mTIM-1 and mTIM-2 receptors revealed an immunoglobulin (Ig) fold, with four Cys residues bridging a distinctive CC' loop to the GFC beta-sheet. The structures showed two ligand-recognition modes in the TIM family. The mTIM-1 structure identified a homophilic TIM-TIM adhesion interaction, whereas the mTIM-2 domain formed a dimer that prevented homophilic binding. Biochemical, mutational, and cell adhesion analyses confirmed the divergent ligand-binding modes revealed by the structures. Structural features characteristic of mTIM-1 appear conserved in human TIM-1, which also mediated homophilic interactions. The extracellular mucin domain enhanced binding through the Ig domain, modulating TIM receptor functions. These results explain the divergent immune functions described for the murine receptors and the role of TIM-1 as a cell adhesion receptor in renal regeneration and cancer.
Figures
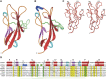
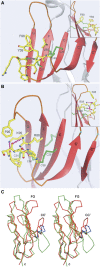

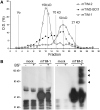
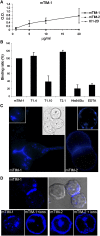
Comment in
-
Tim protein structures reveal a unique face for ligand binding.Immunity. 2007 Mar;26(3):273-5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.03.004. Immunity. 2007. PMID: 17376389 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Characterization of Human and Murine T-Cell Immunoglobulin Mucin Domain 4 (TIM-4) IgV Domain Residues Critical for Ebola Virus Entry.J Virol. 2016 Jun 10;90(13):6097-6111. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00100-16. Print 2016 Jul 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27122575 Free PMC article.
-
Structures of T cell immunoglobulin mucin protein 4 show a metal-Ion-dependent ligand binding site where phosphatidylserine binds.Immunity. 2007 Dec;27(6):941-51. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.11.008. Immunity. 2007. PMID: 18083575 Free PMC article.
-
T cell immunoglobulin mucin-3 crystal structure reveals a galectin-9-independent ligand-binding surface.Immunity. 2007 Mar;26(3):311-21. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.01.016. Immunity. 2007. PMID: 17363302
-
The T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain (Tim) gene family in asthma, allergy, and autoimmunity.Allergy Asthma Proc. 2013 Jan-Feb;34(1):e21-6. doi: 10.2500/aap.2013.34.3646. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2013. PMID: 23406933 Review.
-
Novel roles for TIM-1 in immunity and infection.Immunol Lett. 2011 Dec 30;141(1):28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2011.08.003. Epub 2011 Sep 2. Immunol Lett. 2011. PMID: 21911007 Review.
Cited by
-
Control of signaling-mediated clearance of apoptotic cells by the tumor suppressor p53.Science. 2015 Jul 31;349(6247):1261669. doi: 10.1126/science.1261669. Science. 2015. PMID: 26228159 Free PMC article.
-
TIM-4 is expressed on invariant NKT cells but dispensable for their development and function.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 1;7(44):71099-71111. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12153. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27662666 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosuppressive Mechanisms of Regulatory B Cells.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 29;12:611795. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.611795. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33995344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel antibody targeting TIM-3 resulting in receptor internalization for cancer immunotherapy.Antib Ther. 2020 Nov 9;3(4):227-236. doi: 10.1093/abt/tbaa022. eCollection 2020 Dec. Antib Ther. 2020. PMID: 33928230 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the phosphatidylserine receptor TIM-1 in enveloped-virus entry.J Virol. 2013 Aug;87(15):8327-41. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01025-13. Epub 2013 May 22. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23698310 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

