Identification, activation, and selective in vivo ablation of mouse NK cells via NKp46
- PMID: 17360655
- PMCID: PMC1805551
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0609692104
Identification, activation, and selective in vivo ablation of mouse NK cells via NKp46
Abstract
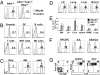
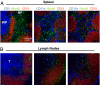
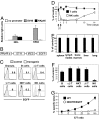
Natural killer (NK) cells contribute to a variety of innate immune responses to viruses, tumors and allogeneic cells. However, our understanding of NK cell biology is severely limited by the lack of consensus phenotypic definition of these cells across species, by the lack of specific marker to visualize them in situ, and by the lack of a genetic model where NK cells may be selectively ablated. NKp46/CD335 is an Ig-like superfamily cell surface receptor involved in human NK cell activation. In addition to human, we show here that NKp46 is expressed by NK cells in all mouse strains analyzed, as well as in three common monkey species, prompting a unifying phenotypic definition of NK cells across species based on NKp46 cell surface expression. Mouse NKp46 triggers NK cell effector function and allows the detection of NK cells in situ. NKp46 expression parallels cell engagement into NK differentiation programs because it is detected on all NK cells from the immature CD122(+)NK1.1(+)DX5(-) stage and on a minute fraction of NK-like T cells, but not on CD1d-restricted NKT cells. Moreover, human NKp46 promoter drives NK cell selective expression both in vitro and in vivo. Using NKp46 promoter, we generated transgenic mice expressing EGFP and the diphtheria toxin (DT) receptor in NK cells. DT injection in these mice leads to a complete and selective NK cell ablation. This model paves a way for the in vivo characterization and preclinical assessment of NK cell biological function.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: M.B., P.A., K.C., L.G., and Y.M. are employees and shareholders of Innate-Pharma. F.R. is founder, employee, and shareholder of Innate-Pharma. E.V. and A.M. are founders and shareholders of Innate-Pharma.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Using Experience Sampling Methodology to Capture Disclosure Opportunities for Autistic Adults.Autism Adulthood. 2023 Dec 1;5(4):389-400. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0090. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Autism Adulthood. 2023. PMID: 38116059 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Qualitative evidence synthesis informing our understanding of people's perceptions and experiences of targeted digital communication.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 23;10(10):ED000141. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000141. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31643081 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Surgical and Nonsurgical Aesthetic Procedures: A 14-Year Analysis of the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery-ISAPS.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Oct;48(20):4217-4227. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04260-2. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 39103642 Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping of NKp46(+) Cells in Healthy Human Lymphoid and Non-Lymphoid Tissues.Front Immunol. 2012 Nov 20;3:344. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00344. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23181063 Free PMC article.
-
PDK1 orchestrates early NK cell development through induction of E4BP4 expression and maintenance of IL-15 responsiveness.J Exp Med. 2015 Feb 9;212(2):253-65. doi: 10.1084/jem.20141703. Epub 2015 Jan 26. J Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 25624444 Free PMC article.
-
Natural killer cell therapies.Nature. 2024 Feb;626(8000):727-736. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06945-1. Epub 2024 Feb 21. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38383621 Review.
-
TGF-β is responsible for NK cell immaturity during ontogeny and increased susceptibility to infection during mouse infancy.Nat Immunol. 2012 Sep;13(9):843-50. doi: 10.1038/ni.2388. Epub 2012 Aug 5. Nat Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22863752 Free PMC article.
-
Lineage relationships of human interleukin-22-producing CD56+ RORγt+ innate lymphoid cells and conventional natural killer cells.Blood. 2013 Mar 21;121(12):2234-43. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-07-440099. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23327921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moretta A, Bottino C, Mingari MC, Biassoni R, Moretta L. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:6–8. - PubMed
-
- Degli-Esposti MA, Smyth MJ. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:112–124. - PubMed
-
- Stewart CA, Vivier E, Colonna M. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006;298:1–21. - PubMed
-
- Moffett-King A. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:656–663. - PubMed
-
- Raulet DH. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:996–1002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

