A role for type 1alpha corticotropin-releasing hormone receptors in mediating local changes in chronically inflamed tissue
- PMID: 17322394
- PMCID: PMC1864887
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.061000
A role for type 1alpha corticotropin-releasing hormone receptors in mediating local changes in chronically inflamed tissue
Abstract
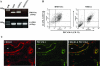
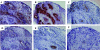
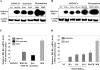
Peripheral corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) is an important regulator of localized inflammatory responses. The aim of this study is to define the pathological signaling pathways in which peripheral CRH receptor-mediated responses reside. We report that PECAM-1-expressing synovial membrane endothelial cells are the principal source of CRH receptor subtype 1alpha in chronically inflamed synovial tissue (ST). Analysis of ST from an early arthritis patient cohort (n = 9) established that expression of CRH-R1alpha significantly (P < 0.03) colocalized with PECAM-1 and E-selectin expression in vivo. Freshly excised ST explants released a mediator(s) that acts to promote CRH-R1alpha mRNA to levels present in inflamed human synovium (n = 8). We tested the ability of conditioned medium and individual inflammatory mediators to modulate CRH-R1alpha expression. Histamine selectively induced the expression of CRH-R1alpha, and these effects were mediated through the histamine receptor type 1. Ectopic expression of CRH-R1alpha in normal human endothelial and synoviocyte cells resulted in the induction of the orphan receptor NR4A2 through the reconstitution of cAMP/protein kinase A/cAMP response element-binding protein signaling and identified a role for CRH in modulating nuclear factor kappaB transcriptional activity. CRH enhanced the expression of nitric-oxide synthase (NOS III) to promote NO production from CRH-R1alpha-expressing cells. These data establish a role for CRH receptor-mediated responses in regulating vascular changes associated with chronic synovitis.
Figures


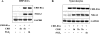
Similar articles
-
Histamine modulation of peripheral CRH receptor type 1alpha expression is dependent on Ca(2+) signalling and NF-kappaB/p65 transcriptional activity.Mol Immunol. 2010 Apr;47(7-8):1426-37. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2010.02.012. Epub 2010 Mar 15. Mol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20233629
-
Corticotropin-releasing hormone signaling in synovial tissue from patients with early inflammatory arthritis is mediated by the type 1 alpha corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor.Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Aug;44(8):1761-7. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200108)44:8<1761::AID-ART311>3.0.CO;2-D. Arthritis Rheum. 2001. PMID: 11508426
-
Involvement of the nuclear orphan receptor NURR1 in the regulation of corticotropin-releasing hormone expression and actions in human inflammatory arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Apr;44(4):782-93. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200104)44:4<782::AID-ANR134>3.0.CO;2-H. Arthritis Rheum. 2001. PMID: 11315917
-
Corticotropin releasing hormone and the skin.Front Biosci. 2006 Sep 1;11:2230-48. doi: 10.2741/1966. Front Biosci. 2006. PMID: 16720310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of corticotropin-releasing hormone in immune-mediated cutaneous inflammatory disease.Exp Dermatol. 2006 Mar;15(3):143-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2006.00382.x. Exp Dermatol. 2006. PMID: 16480421 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurotensin and CRH interactions augment human mast cell activation.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48934. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048934. Epub 2012 Nov 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23155429 Free PMC article.
-
Cell membrane-bound Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded glycoprotein B promotes virus latency by regulating expression of cellular Egr-1.J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 26;285(48):37491-502. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.159103. Epub 2010 Sep 23. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20864524 Free PMC article.
-
Orphan Nuclear Receptor NR4A2 Is Constitutively Expressed in Cartilage and Upregulated in Inflamed Synovium From hTNF-Alpha Transgenic Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 20;13:835697. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.835697. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35529439 Free PMC article.
-
Corticotropin-releasing factor family and its receptors: pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory targets in the periphery?Inflamm Res. 2011 Aug;60(8):715-21. doi: 10.1007/s00011-011-0329-2. Epub 2011 Apr 8. Inflamm Res. 2011. PMID: 21476084 Review.
-
Insights into mechanisms of corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor signal transduction.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 May;166(1):85-97. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01631.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21883143 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fife MS, Fisher SA, John S, Worthington J, Shah CJ, Ollier WE, Panayi GS, Lewis CM, Lanchbury JS. Multipoint linkage analysis of a candidate gene locus in rheumatoid arthritis demonstrates significant evidence of linkage and association with the corticotropin-releasing hormone genomic region. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:1673–1678. - PubMed
-
- Fife M, Steer S, Fisher S, Newton J, McKay K, Worthington J, Shah C, Polley A, Rosenthal A, Ollier W, Lewis C, Wordsworth P, Lanchbury J. Association of familial and sporadic rheumatoid arthritis with a single corticotropin-releasing hormone genomic region (8q12.3) haplotype. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:75–82. - PubMed
-
- Crofford LJ, Sano H, Karalis K, Friedman TC, Epps HR, Remmers EF, Mathern P, Chrousos GP, Wilder RL. Corticotropin-releasing hormone in synovial fluids and tissues of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. J Immunol. 1993;151:1587–1596. - PubMed
-
- Murphy EP, McEvoy A, Conneely OM, Bresnihan B, FitzGerald O. Involvement of the nuclear orphan receptor NURR1 in the regulation of corticotropin-releasing hormone expression and actions in human inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:782–793. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

