TGF-beta dependent regulation of oxygen radicals during transdifferentiation of activated hepatic stellate cells to myofibroblastoid cells
- PMID: 17311678
- PMCID: PMC1804283
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-5926-6-1
TGF-beta dependent regulation of oxygen radicals during transdifferentiation of activated hepatic stellate cells to myofibroblastoid cells
Abstract
Background: The activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) plays a pivotal role during liver injury because the resulting myofibroblasts (MFBs) are mainly responsible for connective tissue re-assembly. MFBs represent therefore cellular targets for anti-fibrotic therapy. In this study, we employed activated HSCs, termed M1-4HSCs, whose transdifferentiation to myofibroblastoid cells (named M-HTs) depends on transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta. We analyzed the oxidative stress induced by TGF-beta and examined cellular defense mechanisms upon transdifferentiation of HSCs to M-HTs.
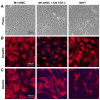
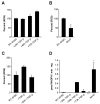
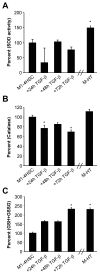
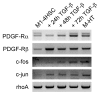
Results: We found reactive oxygen species (ROS) significantly upregulated in M1-4HSCs within 72 hours of TGF-beta administration. In contrast, M-HTs harbored lower intracellular ROS content than M1-4HSCs, despite of elevated NADPH oxidase activity. These observations indicated an upregulation of cellular defense mechanisms in order to protect cells from harmful consequences caused by oxidative stress. In line with this hypothesis, superoxide dismutase activation provided the resistance to augmented radical production in M-HTs, and glutathione rather than catalase was responsible for intracellular hydrogen peroxide removal. Finally, the TGF-beta/NADPH oxidase mediated ROS production correlated with the upregulation of AP-1 as well as platelet-derived growth factor receptor subunits, which points to important contributions in establishing antioxidant defense.
Conclusion: The data provide evidence that TGF-beta induces NADPH oxidase activity which causes radical production upon the transdifferentiation of activated HSCs to M-HTs. Myofibroblastoid cells are equipped with high levels of superoxide dismutase activity as well as glutathione to counterbalance NADPH oxidase dependent oxidative stress and to avoid cellular damage.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Glutathione and antioxidant enzymes serve complementary roles in protecting activated hepatic stellate cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1832(12):2027-34. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.07.008. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23871839
-
Opposing effects of oestradiol and progesterone on intracellular pathways and activation processes in the oxidative stress induced activation of cultured rat hepatic stellate cells.Gut. 2005 Dec;54(12):1782-9. doi: 10.1136/gut.2005.053278. Gut. 2005. PMID: 16284289 Free PMC article.
-
Phagocytosis of apoptotic bodies by hepatic stellate cells induces NADPH oxidase and is associated with liver fibrosis in vivo.Hepatology. 2006 Mar;43(3):435-43. doi: 10.1002/hep.21093. Hepatology. 2006. PMID: 16496318
-
Cooperation of liver cells in health and disease.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001;161:III-XIII, 1-151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56553-3. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11729749 Review.
-
Oxidative Stress and the Aging Brain: From Theory to Prevention.In: Riddle DR, editor. Brain Aging: Models, Methods, and Mechanisms. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2007. Chapter 15. In: Riddle DR, editor. Brain Aging: Models, Methods, and Mechanisms. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2007. Chapter 15. PMID: 21204345 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of NADPH oxidases in the redox biology of liver fibrosis.Redox Biol. 2015 Dec;6:106-111. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.07.005. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Redox Biol. 2015. PMID: 26204504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative damage and TGF-β differentially induce lung epithelial cell sonic hedgehog and tenascin-C expression: implications for the regulation of lung remodelling in idiopathic interstitial lung disease.Int J Exp Pathol. 2011 Feb;92(1):8-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2010.00743.x. Epub 2010 Oct 29. Int J Exp Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21039988 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental obstructive cholestasis: the wound-like inflammatory liver response.Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2008 Nov 3;1(1):6. doi: 10.1186/1755-1536-1-6. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2008. PMID: 19014418 Free PMC article.
-
Doxorubicin-mediated bone loss in breast cancer bone metastases is driven by an interplay between oxidative stress and induction of TGFβ.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 30;8(10):e78043. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078043. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24205081 Free PMC article.
-
Translational approaches: from fatty liver to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul 21;20(27):9038-49. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.9038. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25083077 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Babior BM. NADPH oxidase: an update. Blood. 1999;93:1464–1476. - PubMed
