X chromosome repression by localization of the C. elegans dosage compensation machinery to sites of transcription initiation
- PMID: 17293863
- PMCID: PMC2753834
- DOI: 10.1038/ng1983
X chromosome repression by localization of the C. elegans dosage compensation machinery to sites of transcription initiation
Abstract
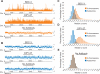
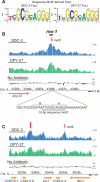
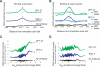
Among organisms with chromosome-based mechanisms of sex determination, failure to equalize expression of X-linked genes between the sexes is typically lethal. In C. elegans, XX hermaphrodites halve transcription from each X chromosome to match the output of XO males. Here, we mapped the binding location of the condensin homolog DPY-27 and the zinc finger protein SDC-3, two components of the C. elegans dosage compensation complex (DCC). We observed strong foci of DCC binding on X, surrounded by broader regions of localization. Binding foci, but not adjacent regions of localization, were distinguished by clusters of a 10-bp DNA motif, suggesting a recruitment-and-spreading mechanism for X recognition. The DCC was preferentially bound upstream of genes, suggesting modulation of transcriptional initiation and polymerase-coupled spreading. Stronger DCC binding upstream of genes with high transcriptional activity indicated a mechanism for tuning DCC activity at specific loci. These data aid in understanding how proteins involved in higher-order chromosome dynamics can regulate transcription at individual loci.
Figures

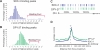
Comment in
-
Think globally, act locally.Nat Genet. 2007 Mar;39(3):287-9. doi: 10.1038/ng0307-287. Nat Genet. 2007. PMID: 17325676 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The C. elegans dosage compensation complex propagates dynamically and independently of X chromosome sequence.Curr Biol. 2009 Nov 17;19(21):1777-87. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.09.047. Epub 2009 Oct 22. Curr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19853451 Free PMC article.
-
Condensin-driven remodelling of X chromosome topology during dosage compensation.Nature. 2015 Jul 9;523(7559):240-4. doi: 10.1038/nature14450. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26030525 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of DCC localization by HTZ-1/H2A.Z and DPY-30 does not correlate with H3K4 methylation levels.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e25973. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025973. Epub 2011 Oct 5. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21998734 Free PMC article.
-
X-Chromosome dosage compensation.WormBook. 2005 Jun 25:1-14. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.8.1. WormBook. 2005. PMID: 18050416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C. elegans dosage compensation: a window into mechanisms of domain-scale gene regulation.Chromosome Res. 2009;17(2):215-27. doi: 10.1007/s10577-008-9011-0. Chromosome Res. 2009. PMID: 19308702 Review.
Cited by
-
The W, X, Y and Z of sex-chromosome dosage compensation.Trends Genet. 2009 May;25(5):226-33. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2009.03.005. Epub 2009 Apr 8. Trends Genet. 2009. PMID: 19359064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dumpy-30 family members as determinants of male fertility and interaction partners of metal-responsive transcription factor 1 (MTF-1) in Drosophila.BMC Dev Biol. 2008 Jun 27;8:68. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-8-68. BMC Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18588663 Free PMC article.
-
A Simple Method for Visualization of Locus-Specific H4K20me1 Modifications in Living Caenorhabditis elegans Single Cells.G3 (Bethesda). 2018 Jul 2;8(7):2249-2255. doi: 10.1534/g3.118.200333. G3 (Bethesda). 2018. PMID: 29724885 Free PMC article.
-
The histone H4 lysine 20 demethylase DPY-21 regulates the dynamics of condensin DC binding.J Cell Sci. 2022 Jan 15;135(2):jcs258818. doi: 10.1242/jcs.258818. Epub 2022 Jan 26. J Cell Sci. 2022. PMID: 34918745 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide views of chromatin structure.Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:245-71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.78.071107.134639. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19317649 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Meyer BJ, Casson LP. Caenorhabditis elegans compensates for the difference in X chromosome dosage between the sexes by regulating transcript levels. Cell. 1986;47:871–81. - PubMed
-
- Chuang PT, Albertson DG, Meyer BJ. DPY-27:a chromosome condensation protein homolog that regulates C. elegans dosage compensation through association with the X chromosome. Cell. 1994;79:459–74. - PubMed
-
- Davis TL, Meyer BJ. SDC-3 coordinates the assembly of a dosage compensation complex on the nematode X chromosome. Development. 1997;124:1019–31. - PubMed
-
- Plath K, Mlynarczyk-Evans S, Nusinow DA, Panning B. Xist RNA and the mechanism of X chromosome inactivation. Annu Rev Genet. 2002;36:233–78. - PubMed
-
- Baugh LR, Hill AA, Slonim DK, Brown EL, Hunter CP. Composition and dynamics of the Caenorhabditis elegans early embryonic transcriptome. Development. 2003;130:889–900. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

