Disease mutations in RUNX1 and RUNX2 create nonfunctional, dominant-negative, or hypomorphic alleles
- PMID: 17290219
- PMCID: PMC1852839
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601568
Disease mutations in RUNX1 and RUNX2 create nonfunctional, dominant-negative, or hypomorphic alleles
Abstract
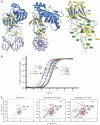
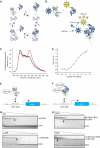
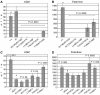
Monoallelic RUNX1 mutations cause familial platelet disorder with predisposition for acute myelogenous leukemia (FPD/AML). Sporadic mono- and biallelic mutations are found at high frequencies in AML M0, in radiation-associated and therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome and AML, and in isolated cases of AML M2, M5a, M3 relapse, and chronic myelogenous leukemia in blast phase. Mutations in RUNX2 cause the inherited skeletal disorder cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD). Most hematopoietic missense mutations in Runx1 involve DNA-contacting residues in the Runt domain, whereas the majority of CCD mutations in Runx2 are predicted to impair CBFbeta binding or the Runt domain structure. We introduced different classes of missense mutations into Runx1 and characterized their effects on DNA and CBFbeta binding by the Runt domain, and on Runx1 function in vivo. Mutations involving DNA-contacting residues severely inactivate Runx1 function, whereas mutations that affect CBFbeta binding but not DNA binding result in hypomorphic alleles. We conclude that hypomorphic RUNX2 alleles can cause CCD, whereas hematopoietic disease requires more severely inactivating RUNX1 mutations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The cleidocranial dysplasia-related R131G mutation in the Runt-related transcription factor RUNX2 disrupts binding to DNA but not CBF-beta.J Cell Biochem. 2010 May;110(1):97-103. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22516. J Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20225274 Free PMC article.
-
Novel RUNX2 mutations in Chinese individuals with cleidocranial dysplasia.J Dent Res. 2009 Sep;88(9):861-6. doi: 10.1177/0022034509342083. J Dent Res. 2009. PMID: 19767586
-
In vitro analyses of known and novel RUNX1/AML1 mutations in dominant familial platelet disorder with predisposition to acute myelogenous leukemia: implications for mechanisms of pathogenesis.Blood. 2002 Feb 15;99(4):1364-72. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.4.1364. Blood. 2002. PMID: 11830488
-
RUNX1 and CBFβ Mutations and Activities of Their Wild-Type Alleles in AML.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;962:265-282. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-3233-2_17. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28299663 Review.
-
Point mutations in the RUNX1/AML1 gene: another actor in RUNX leukemia.Oncogene. 2004 May 24;23(24):4284-96. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207779. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15156185 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetics of familial forms of thrombocytopenia.Hum Genet. 2012 Dec;131(12):1821-32. doi: 10.1007/s00439-012-1215-x. Epub 2012 Aug 11. Hum Genet. 2012. PMID: 22886561 Review.
-
The ability of MLL to bind RUNX1 and methylate H3K4 at PU.1 regulatory regions is impaired by MDS/AML-associated RUNX1/AML1 mutations.Blood. 2011 Dec 15;118(25):6544-52. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-11-317909. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Blood. 2011. PMID: 22012064 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired hematopoietic differentiation of RUNX1-mutated induced pluripotent stem cells derived from FPD/AML patients.Leukemia. 2014 Dec;28(12):2344-54. doi: 10.1038/leu.2014.136. Epub 2014 Apr 15. Leukemia. 2014. PMID: 24732596
-
Cellular and molecular characterization of a novel primary osteoblast culture from the vertebrate model organism Xenopus tropicalis.Histochem Cell Biol. 2015 Apr;143(4):431-42. doi: 10.1007/s00418-014-1289-8. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Histochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25371327
-
Detection of an Abnormal Myeloid Clone by Flow Cytometry in Familial Platelet Disorder With Propensity to Myeloid Malignancy.Am J Clin Pathol. 2016 Feb;145(2):271-6. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqv080. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Am J Clin Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26800764 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berardi M, Sun C, Zehr M, Abildgarrd F, Peng J, Speck NA, Bushweller JH (1999) The Ig fold of the core binding factor a Runt domain is a member of a family of structurally and functionally related Ig-fold DNA-binding domains. Structure 10: 1247–1256 - PubMed
-
- Bravo J, Li Z, Speck NA, Warren AJ (2001) The leukemia-associated AML1 (Runx1)–CBFβ complex functions as a DNA-induced molecular clamp. Nat Struct Biol 8: 371–378 - PubMed
-
- Buijs A, Poddighe P, van Wijk R, van Solinge W, Borst E, Verdonck L, Hagenbeek A, Perason P, Lokhorst H (2001) A novel CBFA2 single-nucleotide mutation in familial platelet disorder with propensity to develop myeloid malignancies. Blood 98: 2856–2858 - PubMed
-
- Bullock AN, Fersht AR (2001) Rescuing the function of mutant p53. Nat Rev Cancer 1: 68–76 - PubMed
-
- Corazza A, Pettirossi F, Viglino P, Verdone G, Garcia J, Dumy P, Giorgetti S, Mangione P, Raimondi S, Stoppini M, Bellotti V, Esposito G (2004) Properties of some variants of human beta2-microglobulin and amyloidogenesis. J Biol Chem 279: 9176–9189 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

