The adenovirus E4 ORF3 protein binds and reorganizes the TRIM family member transcriptional intermediary factor 1 alpha
- PMID: 17287283
- PMCID: PMC1866117
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02629-06
The adenovirus E4 ORF3 protein binds and reorganizes the TRIM family member transcriptional intermediary factor 1 alpha
Abstract
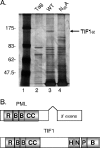
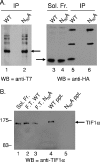
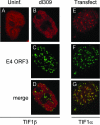
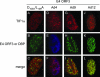
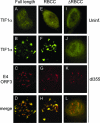
One of the most interesting functions attributed to the adenovirus early region 4 open reading frame 3 (E4 ORF3) protein is its reorganization of promyelocytic leukemia (PML) protein nuclear bodies. These normally punctate structures are reorganized by E4 ORF3 into tracks that eventually surround viral replication centers. PML rearrangement is an evolutionarily conserved function of E4 ORF3, yet its cause and functional relevance remain mysteries. The E4 ORF3 protein coimmunoprecipitates with the PML protein, yet E4 ORF3 still forms tracks in cells that lack PML. The PML protein is a member of a larger protein family termed tripartite motif (TRIM) proteins. TRIM proteins contain a tripartite domain structure in proximity to their N termini that consists of a RING finger domain, followed by one or two B box domains and a C-terminal coiled-coil domain (collectively termed the RBCC domain). The order and spacing of these domains are evolutionarily conserved and thought to mediate protein-protein interactions and other functions. We implemented a proteomic approach to isolate cellular proteins that bind to E4 ORF3. We identified a novel interaction between E4 ORF3 and another TRIM family member, transcriptional intermediary factor 1 alpha (TIF1alpha). TIF1alpha functions by recruiting coactivators and/or corepressors to modulate transcription. The interaction between E4 ORF3 and TIF1alpha was validated by coimmunoprecipitation and binding of recombinant proteins. Indirect immunofluorescence assays demonstrated that TIF1alpha is reorganized into track structures that contain PML upon E4 ORF3 expression. The RBCC domain of TIF1alpha is sufficient for E4 ORF3-induced rearrangement, and TIF1alpha reorganization is conserved across adenovirus serotypes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adenovirus E4 ORF3 protein inhibits the interferon-mediated antiviral response.J Virol. 2007 May;81(9):4744-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02385-06. Epub 2007 Feb 14. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17301128 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Induction of the cellular E2F-1 promoter by the adenovirus E4-6/7 protein.J Virol. 2000 Mar;74(5):2084-93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.5.2084-2093.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10666238 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Trends in Surgical and Nonsurgical Aesthetic Procedures: A 14-Year Analysis of the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery-ISAPS.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Oct;48(20):4217-4227. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04260-2. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 39103642 Review.
Cited by
-
Adenovirus E4-ORF3-dependent relocalization of TIF1α and TIF1γ relies on access to the Coiled-Coil motif.Virology. 2012 Jan 20;422(2):317-25. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2011.10.033. Epub 2011 Nov 27. Virology. 2012. PMID: 22123502 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus E4orf3 targets transcriptional intermediary factor 1γ for proteasome-dependent degradation during infection.J Virol. 2012 Mar;86(6):3167-79. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06583-11. Epub 2011 Dec 28. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22205733 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus Early Proteins and Host Sumoylation.mBio. 2016 Sep 20;7(5):e01154-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01154-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27651358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenovirus late-phase infection is controlled by a novel L4 promoter.J Virol. 2010 Jul;84(14):7096-104. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00107-10. Epub 2010 May 5. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20444889 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Adenovirus E4-ORF3-Mediated SUMO Modifications.mBio. 2019 Feb 26;10(1):e00022-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00022-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30808699 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berk, A. J. 2005. Recent lessons in gene expression, cell cycle control, and cell biology from adenovirus. Oncogene 24:7673-7685. - PubMed
-
- Boyer, J., K. Rohleder, and G. Ketner. 1999. Adenovirus E4 34k and E4 11k inhibit double strand break repair and are physically associated with the cellular DNA-dependent protein kinase. Virology 263:307-312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

