Guinea pig neutrophils infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis produce cytokines which activate alveolar macrophages in noncontact cultures
- PMID: 17283104
- PMCID: PMC1865707
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00858-06
Guinea pig neutrophils infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis produce cytokines which activate alveolar macrophages in noncontact cultures
Abstract
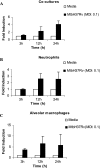
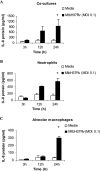
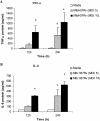
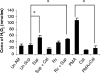
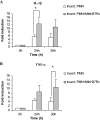
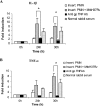
The early influx of neutrophils to the site of infection may be an important step in host resistance against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In this study, we investigated the effect of M. tuberculosis infection on the ability of guinea pig neutrophils to produce interleukin-8 (IL-8; CXCL8) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and to activate alveolar macrophages. Neutrophils and alveolar macrophages were isolated from naïve guinea pigs, cultured together or alone, and infected with virulent M. tuberculosis for 3, 12, and 24 h. IL-8 protein production in cocultures, as measured by using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, was found to be additive at 24 h and significantly greater in M. tuberculosis-infected cocultures than in uninfected cocultures and in cultures of the infected neutrophils or macrophages alone. The IL-8 mRNA levels, determined by real-time reverse transcription-PCR, were elevated at 24 h in infected cocultures and infected cells cultured alone. In order to elucidate the contributions of neutrophils and their soluble mediators to the activation of alveolar macrophages, neutrophils and alveolar macrophages were cultured in a contact-independent manner by using a Transwell insert system. Neutrophils were infected with virulent M. tuberculosis in the upper wells, and alveolar macrophages were cultured in the lower wells. The release of hydrogen peroxide from alveolar macrophages exposed to soluble products from infected neutrophils was significantly increased compared to that from unexposed alveolar macrophages. Significant up-regulation of IL-1beta and TNF-alpha mRNA levels in alveolar macrophages was observed at 24 and 30 h, respectively, compared to those in cells not exposed to soluble neutrophil products. Treatment with anti-guinea pig TNF-alpha polyclonal antibody completely abolished the response of alveolar macrophages to neutrophil products. This finding suggests that TNF-alpha produced by infected neutrophils may be involved in the activation of alveolar macrophages and hence may contribute to the containment of M. tuberculosis infection during the early period of infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Guinea pig neutrophil-macrophage interactions during infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Microbes Infect. 2010 Oct;12(11):828-37. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2010.05.009. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Microbes Infect. 2010. PMID: 20685396 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant guinea pig tumor necrosis factor alpha stimulates the expression of interleukin-12 and the inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth in macrophages.Infect Immun. 2005 Mar;73(3):1367-76. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.3.1367-1376.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15731034 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine-induced cytokine responses in a guinea pig model of pulmonary tuberculosis.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2005 Sep-Nov;85(5-6):295-301. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2005.08.012. Epub 2005 Oct 25. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2005. PMID: 16253558
-
Macrophage immunoregulatory pathways in tuberculosis.Semin Immunol. 2014 Dec;26(6):471-85. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2014.09.010. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Semin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25453226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate immunity, cytokines, and pulmonary host defense.Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1998 Sep;12(3):555-67, vii. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5520(05)70198-7. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1998. PMID: 9779378 Review.
Cited by
-
Guinea pig neutrophil-macrophage interactions during infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Microbes Infect. 2010 Oct;12(11):828-37. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2010.05.009. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Microbes Infect. 2010. PMID: 20685396 Free PMC article.
-
Human Macrophages Activate Bystander Neutrophils' Metabolism and Effector Functions When Challenged with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 1;25(5):2898. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052898. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474145 Free PMC article.
-
Bovine Neutrophils Release Extracellular Traps and Cooperate With Macrophages in Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis clearance In Vitro.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 17;12:645304. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.645304. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33815401 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of copper nanoparticle exposure on host defense in a murine pulmonary infection model.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2011 Sep 24;8:29. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-8-29. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21943386 Free PMC article.
-
Prominent role for T cell-derived tumour necrosis factor for sustained control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection.Sci Rep. 2013;3:1809. doi: 10.1038/srep01809. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23657146 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antony, V. B., S. A. Sahn, R. N. Harada, and J. E. Repine. 1983. Lung repair and granuloma formation. Tubercle bacilli stimulated neutrophils release chemotactic factors for monocytes. Chest 83:95S-96S. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle, P. A., and D. Baltimore. 1996. NF-kappa B: ten years after. Cell 87:13-20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

