Distinct roles of the C2A and the C2B domain of the vesicular Ca2+ sensor synaptotagmin 9 in endocrine beta-cells
- PMID: 17263688
- PMCID: PMC1876385
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20061182
Distinct roles of the C2A and the C2B domain of the vesicular Ca2+ sensor synaptotagmin 9 in endocrine beta-cells
Abstract
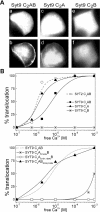
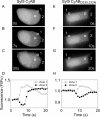
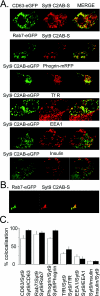
Synaptotagmins form a family of calcium-sensor proteins implicated in exocytosis, and these vesicular transmembrane proteins are endowed with two cytosolic calcium-binding C2 domains, C2A and C2B. Whereas the isoforms syt1 and syt2 have been studied in detail, less is known about syt9, the calcium sensor involved in endocrine secretion such as insulin release from large dense core vesicles in pancreatic beta-cells. Using cell-based assays to closely mimic physiological conditions, we observed SNARE (soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein-attachment protein receptor)-independent translocation of syt9C2AB to the plasma membrane at calcium levels corresponding to endocrine exocytosis, followed by internalization to endosomes. The use of point mutants and truncations revealed that initial translocation required only the C2A domain, whereas the C2B domain ensured partial pre-binding of syt9C2AB to the membrane and post-stimulatory localization to endosomes. In contrast with the known properties of neuronal and neuroendocrine syt1 or syt2, the C2B domain of syt9 did not undergo calcium-dependent membrane binding despite a high degree of structural homology as observed through molecular modelling. The present study demonstrates distinct intracellular properties of syt9 with different roles for each C2 domain in endocrine cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synaptotagmin C2B domain regulates Ca2+-triggered fusion in vitro: critical residues revealed by scanning alanine mutagenesis.J Biol Chem. 2008 Nov 14;283(46):31763-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803355200. Epub 2008 Sep 10. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18784080 Free PMC article.
-
Polybasic Patches in Both C2 Domains of Synaptotagmin-1 Are Required for Evoked Neurotransmitter Release.J Neurosci. 2022 Jul 27;42(30):5816-5829. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1385-21.2022. Epub 2022 Jun 14. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35701163 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and mutational analysis of functional differentiation between synaptotagmins-1 and -7.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 2;5(9):e12544. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012544. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20824061 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane resealing: synaptotagmin VII keeps running the show.Sci STKE. 2005 May 3;2005(282):pe19. doi: 10.1126/stke.2822005pe19. Sci STKE. 2005. PMID: 15870423 Review.
-
Synaptotagmins bind calcium to release insulin.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Dec;295(6):E1279-86. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.90568.2008. Epub 2008 Aug 19. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008. PMID: 18713958 Review.
Cited by
-
Hydrophobic contributions to the membrane docking of synaptotagmin 7 C2A domain: mechanistic contrast between isoforms 1 and 7.Biochemistry. 2012 Oct 2;51(39):7654-64. doi: 10.1021/bi3007115. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22966849 Free PMC article.
-
Novel aspects of the molecular mechanisms controlling insulin secretion.J Physiol. 2008 Jul 15;586(14):3313-24. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.155317. Epub 2008 May 29. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18511483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silencing of synaptotagmin 13 inhibits tumor growth through suppressing proliferation and promoting apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells.Int J Mol Med. 2020 Jan;45(1):234-244. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4412. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31939613 Free PMC article.
-
Role of calcium and EPAC in norepinephrine-induced ghrelin secretion.Endocrinology. 2014 Jan;155(1):98-107. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1691. Epub 2013 Dec 20. Endocrinology. 2014. PMID: 24189139 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotransmitters regulate β cells insulin secretion: A neglected factor.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Oct 6;11(28):6670-6679. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i28.6670. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 37901031 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Henquin J. C. Pathways in β-cell stimulus-secretion coupling as targets for therapeutic insulin secretagogues. Diabetes. 2004;53:S48–S58. - PubMed
-
- Lang J. Molecular mechanisms and regulation of insulin exocytosis as a paradigm of endocrine secretion. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999;259:3–17. - PubMed
-
- Jahn R., Lang T., Sudhof T. C. Membrane fusion. Cell. 2003;112:519–533. - PubMed
-
- Sudhof T. C. The synaptic vesicle cycle. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2004;27:509–547. - PubMed
-
- Bhalla A., Chicka M. C., Tucker W. C., Chapman E. R. Ca2+-synaptotagmin directly regulates t-SNARE function during reconstituted membrane fusion. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006;13:323–330. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

