Rat cytomegalovirus gene expression in cardiac allograft recipients is tissue specific and does not parallel the profiles detected in vitro
- PMID: 17251289
- PMCID: PMC1866122
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02425-06
Rat cytomegalovirus gene expression in cardiac allograft recipients is tissue specific and does not parallel the profiles detected in vitro
Abstract
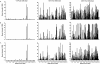
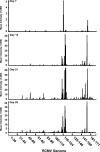
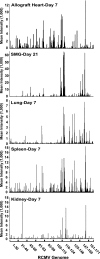
Rat cytomegalovirus (RCMV) is a beta-herpesvirus with a 230-kbp genome containing over 167 open reading frames (ORFs). RCMV gene expression is tightly regulated in cultured cells, occurring in three distinct kinetic classes (immediate early, early, and late). However, the extent of viral-gene expression in vivo and its relationship to the in vitro expression are unknown. In this study, we used RCMV-specific DNA microarrays to investigate the viral transcriptional profiles in cultured, RCMV-infected endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and aortic smooth muscle cells and to compare these profiles to those found in tissues from RCMV-infected rat heart transplant recipients. In cultured cells, RCMV expresses approximately 95% of the known viral ORFs with few differences between cell types. By contrast, in vivo viral-gene expression in tissues from rat heart allograft recipients is highly restricted. In the tissues studied, a total of 80 viral genes expressing levels twice above background (5,000 to 10,000 copies per mug total RNA) were detected. In each tissue type, there were a number of genes expressed exclusively in that tissue. Although viral mRNA and genomic DNA levels were lower in the spleen than in submandibular glands, the number of individual viral genes expressed was higher in the spleen (60 versus 41). This finding suggests that the number of viral genes expressed is specific to a given tissue and is not dependent upon the viral load or viral mRNA levels. Our results demonstrate that the profiles, as well as the amplitude, of viral-gene expression are tissue specific and are dramatically different from those in infected cultured cells, indicating that RCMV gene expression in vitro does not reflect viral-gene expression in vivo.
Figures

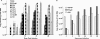
Similar articles
-
Cytomegalovirus microRNA expression is tissue specific and is associated with persistence.J Virol. 2011 Jan;85(1):378-89. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01900-10. Epub 2010 Oct 27. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 20980502 Free PMC article.
-
The rat cytomegalovirus R78 G protein-coupled receptor gene is required for production of infectious virus in the spleen.J Gen Virol. 2003 Sep;84(Pt 9):2517-2530. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.19227-0. J Gen Virol. 2003. PMID: 12917474
-
A rat cytomegalovirus strain with a disruption of the r144 MHC class I-like gene is attenuated in the acute phase of infection in neonatal rats.Arch Virol. 2002 Apr;147(4):813-24. doi: 10.1007/s007050200028. Arch Virol. 2002. PMID: 12038690
-
Identification and comparison of RCMV ALL 03 open reading frame (ORF) among several different strains of cytomegalovirus worldwide.Infect Genet Evol. 2017 Oct;54:81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2017.06.020. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Infect Genet Evol. 2017. PMID: 28642159
-
Rat cytomegalovirus-accelerated transplant vascular sclerosis is reduced with mutation of the chemokine-receptor R33.Am J Transplant. 2005 Mar;5(3):436-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2004.00711.x. Am J Transplant. 2005. PMID: 15707397
Cited by
-
Functional genomics approaches to understand cytomegalovirus replication, latency and pathogenesis.Curr Opin Virol. 2013 Aug;3(4):408-15. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2013.06.002. Epub 2013 Jun 29. Curr Opin Virol. 2013. PMID: 23816389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Memory inflation during chronic viral infection is maintained by continuous production of short-lived, functional T cells.Immunity. 2008 Oct 17;29(4):650-9. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.07.017. Immunity. 2008. PMID: 18957267 Free PMC article.
-
Cytomegalovirus CC chemokine promotes immune cell migration.J Virol. 2012 Nov;86(21):11833-44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00452-12. Epub 2012 Aug 22. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22915808 Free PMC article.
-
Simian varicella virus gene expression during acute and latent infection of rhesus macaques.J Neurovirol. 2011 Dec;17(6):600-12. doi: 10.1007/s13365-011-0057-y. Epub 2011 Nov 4. J Neurovirol. 2011. PMID: 22052378 Free PMC article.
-
Cytomegalovirus microRNA expression is tissue specific and is associated with persistence.J Virol. 2011 Jan;85(1):378-89. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01900-10. Epub 2010 Oct 27. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 20980502 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bresnahan, W. A., and T. Shenk. 2000. A subset of viral transcripts packaged within human cytomegalovirus particles. Science 288:2373-2376. - PubMed
-
- Bruggeman, C. A., W. M. Debie, G. Grauls, G. Majoor, and C. P. van Boven. 1983. Infection of laboratory rats with a new cytomegalo-like virus. Arch. Virol. 76:189-199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

