Structure of the C-terminal half of UvrC reveals an RNase H endonuclease domain with an Argonaute-like catalytic triad
- PMID: 17245438
- PMCID: PMC1783470
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601497
Structure of the C-terminal half of UvrC reveals an RNase H endonuclease domain with an Argonaute-like catalytic triad
Abstract
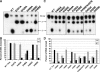
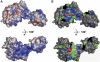
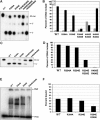
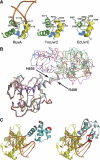
Removal and repair of DNA damage by the nucleotide excision repair pathway requires two sequential incision reactions, which are achieved by the endonuclease UvrC in eubacteria. Here, we describe the crystal structure of the C-terminal half of UvrC, which contains the catalytic domain responsible for 5' incision and a helix-hairpin-helix-domain that is implicated in DNA binding. Surprisingly, the 5' catalytic domain shares structural homology with RNase H despite the lack of sequence homology and contains an uncommon DDH triad. The structure also reveals two highly conserved patches on the surface of the protein, which are not related to the active site. Mutations of residues in one of these patches led to the inability of the enzyme to bind DNA and severely compromised both incision reactions. Based on our results, we suggest a model of how UvrC forms a productive protein-DNA complex to excise the damage from DNA.
Figures
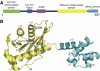

Similar articles
-
Structural insights into the first incision reaction during nucleotide excision repair.EMBO J. 2005 Mar 9;24(5):885-94. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600568. Epub 2005 Feb 3. EMBO J. 2005. PMID: 15692561 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminal region of the UvrB protein of Escherichia coli contains an important determinant for UvrC binding to the preincision complex but not the catalytic site for 3'-incision.J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 22;270(51):30508-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.51.30508. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 8530482
-
The C-terminal region of the Escherichia coli UvrC protein, which is homologous to the C-terminal region of the human ERCC1 protein, is involved in DNA binding and 5'-incision.Nucleic Acids Res. 1998 Jan 15;26(2):462-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.2.462. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998. PMID: 9421501 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional structural views of damaged-DNA recognition: T4 endonuclease V, E. coli Vsr protein, and human nucleotide excision repair factor XPA.Mutat Res. 2000 Aug 30;460(3-4):257-75. doi: 10.1016/s0921-8777(00)00031-8. Mutat Res. 2000. PMID: 10946233 Review.
-
The nucleotide excision repair protein UvrB, a helicase-like enzyme with a catch.Mutat Res. 2000 Aug 30;460(3-4):277-300. doi: 10.1016/s0921-8777(00)00032-x. Mutat Res. 2000. PMID: 10946234 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring damage recognition models in prokaryotic nucleotide excision repair with a benzo[a]pyrene-derived lesion in UvrB.Biochemistry. 2009 Sep 29;48(38):8948-57. doi: 10.1021/bi9010072. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19681599 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperative damage recognition by UvrA and UvrB: identification of UvrA residues that mediate DNA binding.DNA Repair (Amst). 2008 Mar 1;7(3):392-404. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2007.11.013. Epub 2008 Jan 11. DNA Repair (Amst). 2008. PMID: 18248777 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the effect of pulsed light on the protein of Lactobacillus plantarum based on liquid mass spectrometry.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2023 Jul 16;33(3):617-624. doi: 10.1007/s10068-023-01365-3. eCollection 2024 Feb. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38274179 Free PMC article.
-
Collaborative dynamic DNA scanning by nucleotide excision repair proteins investigated by single- molecule imaging of quantum-dot-labeled proteins.Mol Cell. 2010 Mar 12;37(5):702-13. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.02.003. Mol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20227373 Free PMC article.
-
UvrC Coordinates an O2-Sensitive [4Fe4S] Cofactor.J Am Chem Soc. 2020 Jun 24;142(25):10964-10977. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c01671. Epub 2020 Jun 12. J Am Chem Soc. 2020. PMID: 32470300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ariyoshi M, Vassylyev DG, Iwasaki H, Nakamura H, Shinagawa H, Morikawa K (1994) Atomic structure of the RuvC resolvase: a Holliday junction-specific endonuclease from E. coli. Cell 78: 1063–1072 - PubMed
-
- Davies DR, Goryshin IY, Reznikoff WS, Rayment I (2000) Three-dimensional structure of the Tn5 synaptic complex transposition intermediate. Science 289: 77–85 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

