Acetaminophen potentiates staurosporine-induced death in a human neuroblastoma cell line
- PMID: 17245372
- PMCID: PMC2189768
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706993
Acetaminophen potentiates staurosporine-induced death in a human neuroblastoma cell line
Abstract
Background and purpose: Neuroblastoma is the most common solid tumour in infants characterized by a high resistance to apoptosis. Recently, the cyclo-oxygenase pathway has been considered a potential target in the treatment of different kinds of tumours. The aim of the present work was to investigate a possible relationship between cyclo-oxygenase pathway and stauroporine-induced apoptosis in the neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y.
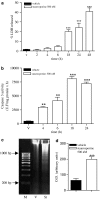
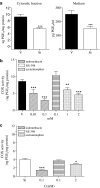
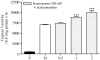
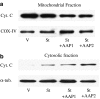
Experimental approach: Cellular viability was measured by release of LDH. DNA fragmentation was visualized by electrophoresis on agarose gel containing ethidium bromide. Cyclo-oxygenase activity was measured in microsomal fractions obtained from cells by quantification of its final product PGE2 by RIA. Caspase-3 activity was measured fluorimetrically and Western blot analysis was performed to assess cytochrome c expression.
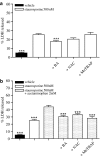
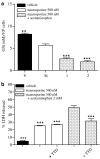
Key results: We have found that staurosporine (500 nM) induced cellular death in a time-dependent manner in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Cyclo-oxygenase enzymatic activity was present in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells under basal conditions and pharmacological experiments using COX inhibitors indicate that cyclo-oxygenase-1 and cyclo-oxygenase-3 are the active isoforms in these cells. Co-incubation of SH-SY5Y cells with staurosporine (500 nM) and acetaminophen for 24 h potentiated staurosporine-mediated cellular death in a concentration-dependent manner. This process is mediated by an increase in cytochrome c release and caspase 3 activation and is prevented by N-acetylcysteine or the superoxide dismutase mimetic, MnTBAP.
Conclusions and implications: Acetaminophen potentiates staurosporine-mediated neuroblastoma cell death. The mechanism of action of acetaminophen seems to be related to production of reactive oxygen species and decreased intracellular glutathione levels.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sodium valproate potentiates staurosporine-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells via Akt/survivin independently of HDAC inhibition.J Cell Biochem. 2013 Apr;114(4):854-63. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24422. J Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23097134
-
Mitochondrial isocitrate dehydrogenase protects human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells against oxidative stress.J Neurosci Res. 2007 Jan;85(1):139-52. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21106. J Neurosci Res. 2007. PMID: 17075901
-
Staurosporine-induced apoptosis presents with unexpected cholinergic effects in a differentiated neuroblastoma cell line.Neurochem Int. 2012 Dec;61(7):1011-20. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2012.07.018. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Neurochem Int. 2012. PMID: 22841891
-
Protective effects of TRH and its analogues against various cytotoxic agents in retinoic acid (RA)-differentiated human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells.Neuropeptides. 2010 Dec;44(6):495-508. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2010.08.004. Neuropeptides. 2010. PMID: 20869113
-
Acetaminophen and the cyclooxygenase-3 puzzle: sorting out facts, fictions, and uncertainties.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Oct;315(1):1-7. doi: 10.1124/jpet.105.085431. Epub 2005 May 6. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005. PMID: 15879007 Review.
Cited by
-
The anti-tumour activity of DNA methylation inhibitor 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine is enhanced by the common analgesic paracetamol through induction of oxidative stress.Cancer Lett. 2021 Mar 31;501:172-186. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.12.029. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Cancer Lett. 2021. PMID: 33359448 Free PMC article.
-
Acetaminophen induces JNK/p38 signaling and activates the caspase-9-3-dependent cell death pathway in human mesenchymal stem cells.Int J Mol Med. 2015 Aug;36(2):485-92. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2254. Epub 2015 Jun 19. Int J Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26096646 Free PMC article.
-
Acetaminophen enhances cisplatin- and paclitaxel-mediated cytotoxicity to SKOV3 human ovarian carcinoma.Anticancer Res. 2013 Jun;33(6):2391-400. Anticancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23749887 Free PMC article.
-
Acetaminophen induces apoptosis in rat cortical neurons.PLoS One. 2010 Dec 10;5(12):e15360. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015360. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21170329 Free PMC article.
-
The endoplasmic reticulum stress and the HIF-1 signalling pathways are involved in the neuronal damage caused by chemical hypoxia.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Jun;172(11):2838-51. doi: 10.1111/bph.13095. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25625917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akundi RS, Candelario-Jalil E, Hess S, Hull M, Lieb K, Gebicke-Haerter PJ, et al. Signal transduction pathways regulating cyclooxygenase-2 in lipopolysaccharide-activated primary rat microglia. Glia. 2005;51:199–208. - PubMed
-
- Boix J, Llecha N, Yuste VJ, Comella JX. Characterization of the cell death process induced by staurosporine in human neuroblastoma cell lines. Neuropharmacology. 1997;36:811–821. - PubMed
-
- Brand MD, Affourtit C, Esteves TC, Green K, Lambert AJ, Miwa S, et al. Mitochondrial superoxide: production, biological effects, and activation of uncoupling proteins. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004;37:755–767. - PubMed
-
- Burcham PC, Harman AW. Acetaminophen toxicity results in site-specific mitochondrial damage in isolated mouse hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:5049–5054. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

