MicroRNA-155 is induced during the macrophage inflammatory response
- PMID: 17242365
- PMCID: PMC1780072
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0610731104
MicroRNA-155 is induced during the macrophage inflammatory response
Abstract
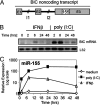
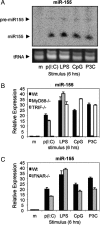
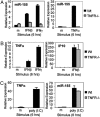
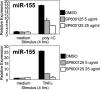
The mammalian inflammatory response to infection involves the induction of several hundred genes, a process that must be carefully regulated to achieve pathogen clearance and prevent the consequences of unregulated expression, such as cancer. Recently, microRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as a class of gene expression regulators that has also been linked to cancer. However, the relationship between inflammation, innate immunity, and miRNA expression is just beginning to be explored. In the present study, we use microarray technology to identify miRNAs induced in primary murine macrophages after exposure to polyriboinosinic:polyribocytidylic acid or the cytokine IFN-beta. miR-155 was the only miRNA of those tested that was substantially up-regulated by both stimuli. It also was induced by several Toll-like receptor ligands through myeloid differentiation factor 88- or TRIF-dependent pathways, whereas up-regulation by IFNs was shown to involve TNF-alpha autocrine signaling. Pharmacological inhibition of the kinase JNK blocked induction of miR-155 in response to either polyriboinosinic:polyribocytidylic acid or TNF-alpha, suggesting that miR-155-inducing signals use the JNK pathway. Together, these findings characterize miR-155 as a common target of a broad range of inflammatory mediators. Importantly, because miR-155 is known to function as an oncogene, these observations identify a potential link between inflammation and cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
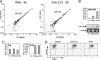
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-132 potentiates cholinergic anti-inflammatory signaling by targeting acetylcholinesterase.Immunity. 2009 Dec 18;31(6):965-73. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.09.019. Epub 2009 Dec 10. Immunity. 2009. PMID: 20005135
-
Phosphatase PTP1B negatively regulates MyD88- and TRIF-dependent proinflammatory cytokine and type I interferon production in TLR-triggered macrophages.Mol Immunol. 2008 Aug;45(13):3545-52. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.05.006. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Mol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18571728
-
Induction of microRNA-155 during Helicobacter pylori infection and its negative regulatory role in the inflammatory response.J Infect Dis. 2009 Sep 15;200(6):916-25. doi: 10.1086/605443. J Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19650740
-
MicroRNAs and immunity: novel players in the regulation of normal immune function and inflammation.Semin Cancer Biol. 2008 Apr;18(2):131-40. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.01.005. Epub 2008 Jan 15. Semin Cancer Biol. 2008. PMID: 18291670 Review.
-
MicroRNAs: novel regulators in skin inflammation.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2008 May;33(3):312-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.2008.02804.x. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18419608 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA viruses and the host microRNA machinery.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013 Mar;11(3):169-80. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2971. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23411862 Review.
-
The relationship between microRNAs and COVID-19 complications.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Aug 22;10:16-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.08.007. eCollection 2025 Feb. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 39296641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HCV-induced miR-21 contributes to evasion of host immune system by targeting MyD88 and IRAK1.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(4):e1003248. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003248. Epub 2013 Apr 25. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23633945 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of miR-99a-5p prevents allergen-driven airway exacerbations without compromising type-2 memory responses in the intestine following helminth infection.Mucosal Immunol. 2021 Jul;14(4):912-922. doi: 10.1038/s41385-021-00401-x. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Mucosal Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33846533 Free PMC article.
-
Association between miRNA-145 and miRNA-155 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with multiple sclerosis: a case-control study.BMC Neurol. 2022 Nov 3;22(1):405. doi: 10.1186/s12883-022-02909-6. BMC Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36329419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira S, Takeda K. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:499–511. - PubMed
-
- Modlin RL, Cheng G. Nat Med. 2004;10:1173–1174. - PubMed
-
- Dunne A, O'Neill LA. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:3330–3335. - PubMed
-
- Doyle S, Vaidya S, O'Connell R, Dadgostar H, Dempsey P, Wu T, Rao G, Sun R, Haberland M, Modlin R, Cheng G. Immunity. 2002;17:251–263. - PubMed
-
- Kracht M, Saklatvala J. Cytokine. 2002;20:91–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

