Coupled release of eukaryotic translation initiation factors 5B and 1A from 80S ribosomes following subunit joining
- PMID: 17242201
- PMCID: PMC1820483
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.02254-06
Coupled release of eukaryotic translation initiation factors 5B and 1A from 80S ribosomes following subunit joining
Abstract
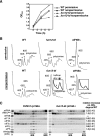
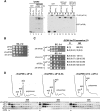
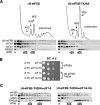
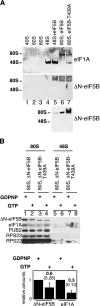
The translation initiation GTPase eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5B (eIF5B) binds to the factor eIF1A and catalyzes ribosomal subunit joining in vitro. We show that rapid depletion of eIF5B in Saccharomyces cerevisiae results in the accumulation of eIF1A and mRNA on 40S subunits in vivo, consistent with a defect in subunit joining. Substituting Ala for the last five residues in eIF1A (eIF1A-5A) impairs eIF5B binding to eIF1A in cell extracts and to 40S complexes in vivo. Consistently, overexpression of eIF5B suppresses the growth and translation initiation defects in yeast expressing eIF1A-5A, indicating that eIF1A helps recruit eIF5B to the 40S subunit prior to subunit joining. The GTPase-deficient eIF5B-T439A mutant accumulated on 80S complexes in vivo and was retained along with eIF1A on 80S complexes formed in vitro. Likewise, eIF5B and eIF1A remained associated with 80S complexes formed in the presence of nonhydrolyzable GDPNP, whereas these factors were released from the 80S complexes in assays containing GTP. We propose that eIF1A facilitates the binding of eIF5B to the 40S subunit to promote subunit joining. Following 80S complex formation, GTP hydrolysis by eIF5B enables the release of both eIF5B and eIF1A, and the ribosome enters the elongation phase of protein synthesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interaction between eukaryotic initiation factors 1A and 5B is required for efficient ribosomal subunit joining.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 31;281(13):8469-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600210200. Epub 2006 Feb 3. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16461768
-
X-ray structures of eIF5B and the eIF5B-eIF1A complex: the conformational flexibility of eIF5B is restricted on the ribosome by interaction with eIF1A.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014 Dec 1;70(Pt 12):3090-8. doi: 10.1107/S1399004714021476. Epub 2014 Nov 22. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014. PMID: 25478828
-
Domains of eIF1A that mediate binding to eIF2, eIF3 and eIF5B and promote ternary complex recruitment in vivo.EMBO J. 2003 Jan 15;22(2):193-204. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg030. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12514125 Free PMC article.
-
The scanning mechanism of eukaryotic translation initiation.Annu Rev Biochem. 2014;83:779-812. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060713-035802. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Annu Rev Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24499181 Review.
-
Functional significance and mechanism of eIF5-promoted GTP hydrolysis in eukaryotic translation initiation.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001;70:207-31. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(01)70018-9. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11642363 Review.
Cited by
-
'Ribozoomin'--translation initiation from the perspective of the ribosome-bound eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs).Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012 Jun;13(4):305-30. doi: 10.2174/138920312801619385. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012. PMID: 22708493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Established and Emerging Regulatory Roles of Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 5B (eIF5B).Front Genet. 2021 Aug 27;12:737433. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.737433. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34512736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
rRNA suppressor of a eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5B/initiation factor 2 mutant reveals a binding site for translational GTPases on the small ribosomal subunit.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Feb;29(3):808-21. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00896-08. Epub 2008 Nov 24. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19029250 Free PMC article.
-
The Jigsaw Puzzle of mRNA Translation Initiation in Eukaryotes: A Decade of Structures Unraveling the Mechanics of the Process.Annu Rev Biophys. 2018 May 20;47:125-151. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-070816-034034. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Annu Rev Biophys. 2018. PMID: 29494255 Free PMC article.
-
Rps5-Rps16 communication is essential for efficient translation initiation in yeast S. cerevisiae.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jul;42(13):8537-55. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku550. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24948608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acker, M. G., B. S. Shin, T. E. Dever, and J. R. Lorsch. 2006. Interaction between eukaryotic initiation factors 1A and 5B is required for efficient ribosomal subunit joining. J. Biol. Chem. 281:8469-8475. - PubMed
-
- Algire, M. A., D. Maag, and J. R. Lorsch. 2005. Pi release from eIF2, not GTP hydrolysis, is the step controlled by start-site selection during eukaryotic translation initiation. Mol. Cell 20:251-262. - PubMed
-
- Allen, G. S., A. Zavialov, R. Gursky, M. Ehrenberg, and J. Frank. 2005. The cryo-EM structure of a translation initiation complex from Escherichia coli. Cell 121:703-712. - PubMed
-
- Battiste, J. B., T. V. Pestova, C. U. T. Hellen, and G. Wagner. 2000. The eIF1A solution structure reveals a large RNA-binding surface important for scanning function. Mol. Cell 5:109-119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
