A large-scale genetic association study confirms IL12B and leads to the identification of IL23R as psoriasis-risk genes
- PMID: 17236132
- PMCID: PMC1785338
- DOI: 10.1086/511051
A large-scale genetic association study confirms IL12B and leads to the identification of IL23R as psoriasis-risk genes
Abstract
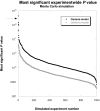
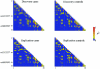
We performed a multitiered, case-control association study of psoriasis in three independent sample sets of white North American individuals (1,446 cases and 1,432 controls) with 25,215 genecentric single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and found a highly significant association with an IL12B 3'-untranslated-region SNP (rs3212227), confirming the results of a small Japanese study. This SNP was significant in all three sample sets (odds ratio [OR](common) 0.64, combined P [Pcomb]=7.85x10(-10)). A Monte Carlo simulation to address multiple testing suggests that this association is not a type I error. The coding regions of IL12B were resequenced in 96 individuals with psoriasis, and 30 additional IL12B-region SNPs were genotyped. Haplotypes were estimated, and genotype-conditioned analyses identified a second risk allele (rs6887695) located approximately 60 kb upstream of the IL12B coding region that exhibited association with psoriasis after adjustment for rs3212227. Together, these two SNPs mark a common IL12B risk haplotype (OR(common) 1.40, Pcomb=8.11x10(-9)) and a less frequent protective haplotype (OR(common) 0.58, Pcomb=5.65x10(-12)), which were statistically significant in all three studies. Since IL12B encodes the common IL-12p40 subunit of IL-12 and IL-23, we individually genotyped 17 SNPs in the genes encoding the other chains of these cytokines (IL12A and IL23A) and their receptors (IL12RB1, IL12RB2, and IL23R). Haplotype analyses identified two IL23R missense SNPs that together mark a common psoriasis-associated haplotype in all three studies (OR(common) 1.44, Pcomb=3.13x10(-6)). Individuals homozygous for both the IL12B and the IL23R predisposing haplotypes have an increased risk of disease (OR(common) 1.66, Pcomb=1.33x10(-8)). These data, and the previous observation that administration of an antibody specific for the IL-12p40 subunit to patients with psoriasis is highly efficacious, suggest that these genes play a fundamental role in psoriasis pathogenesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IL12B and IL23R gene SNPs in Japanese psoriasis.Immunogenetics. 2013 Nov;65(11):823-8. doi: 10.1007/s00251-013-0721-x. Epub 2013 Aug 17. Immunogenetics. 2013. PMID: 23955419
-
Polymorphisms of the IL12B and IL23R genes are associated with psoriasis.J Invest Dermatol. 2008 Jul;128(7):1653-61. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5701255. Epub 2008 Jan 24. J Invest Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18219280 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of association of the IL12B and IL23R genes with psoriatic arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Dec;58(12):3705-9. doi: 10.1002/art.24128. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 19035472 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of IL12B polymorphisms (rs3212227, rs6887695) with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2013 Jul;33(7):1785-90. doi: 10.1007/s00296-012-2637-4. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Rheumatol Int. 2013. PMID: 23297015 Review.
-
Genetic variations in cytokines and cytokine receptors associated with psoriasis found by genome-wide association.J Invest Dermatol. 2009 Apr;129(4):827-33. doi: 10.1038/jid.2008.308. Epub 2008 Oct 2. J Invest Dermatol. 2009. PMID: 18830267 Review.
Cited by
-
Th17-related genes and celiac disease susceptibility.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31244. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031244. Epub 2012 Feb 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22359581 Free PMC article.
-
Microbes, the gut and ankylosing spondylitis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(3):214. doi: 10.1186/ar4228. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 23750937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ustekinumab in psoriasis immunopathology with emphasis on the Th17-IL23 axis: a primer.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:147413. doi: 10.1155/2012/147413. Epub 2012 Jun 12. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22754278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Epidemiology of Psoriasis.Curr Dermatol Rep. 2014 Mar;3(1):61-78. doi: 10.1007/s13671-013-0066-6. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2014. PMID: 25580373 Free PMC article.
-
Pouring fuel on the fire: Th17 cells, the environment, and autoimmunity.J Clin Invest. 2015 Jun;125(6):2211-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI78085. Epub 2015 May 11. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 25961452 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Web Resources
-
- dbSNP, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/SNP/ (for SNPs rs10035989, rs1109918, rs11171806, rs11209026, rs11575926, rs11744690, rs1368437, rs1422668, rs1422878, rs1433048, rs17860508,rs1833754, rs1884444, rs1897565, rs2043270, rs2161357,rs2227314, rs2243131, rs2243149, rs2243154, rs2371494,rs270654, rs270661, rs2914119, rs3212220, rs3212227, rs3213096, rs3213119, rs375947, rs393548, rs401502, rs4921226, rs4921496, rs583911, rs6556398, rs6771983, rs6869411, rs6887695, rs6896438, rs6897374, rs6898290, rs717925, rs7530511, rs7709212, rs7721001, rs918520, rs929779, rs953861, and ss52085990)
-
- Entrez Nucleotide, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?CMD=search&DB=nucleotide (for 5,000 bp upstream of the 5′-most exon of IL12B [accession number NW_922784] and chromosome 5 genomic contig [accession number NT_023133])
-
- Genetic Association Database, http://geneticassociationdb.nih.gov/
-
- HapMap, http://www.hapmap.org/
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for PSORS1, IL12B, IL23R, and mycobacterial disease)
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

