AMPK-mediated inhibition of mTOR kinase is circumvented during immediate-early times of human cytomegalovirus infection
- PMID: 17215282
- PMCID: PMC1866081
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02079-06
AMPK-mediated inhibition of mTOR kinase is circumvented during immediate-early times of human cytomegalovirus infection
Abstract
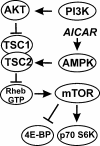
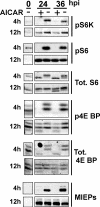
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection increases synthetic rates in infected cells. The resulting increase in energy utilization could potentially increase the AMP:ATP ratio, causing activation of 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Activated AMPK promotes inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) kinase, which could be deleterious to the viral infection. Using the AMPK-activating drug 5-amino-4-imidazolecarboxamide ribose (AICAR), we showed that, by 12 h post-HCMV infection, inhibition of mTOR by AMPK is circumvented. However, growth curves showed that progeny virion production is inhibited when AICAR is added, suggesting other inhibitory effects of AICAR or activated AMPK.
Figures
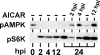

Similar articles
-
Role of adenosine 5'-monophosphate-activated protein kinase subunits in skeletal muscle mammalian target of rapamycin signaling.Mol Endocrinol. 2008 May;22(5):1105-12. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0448. Epub 2008 Feb 14. Mol Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18276828 Free PMC article.
-
Digitoxin Suppresses Human Cytomegalovirus Replication via Na+, K+/ATPase α1 Subunit-Dependent AMP-Activated Protein Kinase and Autophagy Activation.J Virol. 2018 Feb 26;92(6):e01861-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01861-17. Print 2018 Mar 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29321306 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase inhibits growth of multiple myeloma cells.Exp Cell Res. 2007 Oct 1;313(16):3592-603. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.06.020. Epub 2007 Jul 4. Exp Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17669398
-
mTOR integrates amino acid- and energy-sensing pathways.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Jan 9;313(2):443-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.07.019. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 14684182 Review.
-
[5'-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase and lifestyle-mediated diseases].Ugeskr Laeger. 2006 Feb 27;168(9):896-900. Ugeskr Laeger. 2006. PMID: 16513051 Review. Danish.
Cited by
-
Dynein mediates the localization and activation of mTOR in normal and human cytomegalovirus-infected cells.Genes Dev. 2012 Sep 15;26(18):2015-26. doi: 10.1101/gad.196147.112. Genes Dev. 2012. PMID: 22987636 Free PMC article.
-
Can a metabolism-targeted therapeutic intervention successfully subjugate SARS-COV-2? A scientific rational.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Nov;131:110694. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110694. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32920511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infection with HIV and HCV enhances the release of fatty acid synthase into circulation: evidence for a novel indicator of viral infection.BMC Gastroenterol. 2010 Aug 13;10:92. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-10-92. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20707918 Free PMC article.
-
New cell-signaling pathways for controlling cytomegalovirus replication.Am J Transplant. 2014 Jun;14(6):1249-58. doi: 10.1111/ajt.12725. Epub 2014 May 19. Am J Transplant. 2014. PMID: 24839861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subversion of Host Responses to Energy Insufficiency by Us3 Supports Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Replication during Stress.J Virol. 2017 Jun 26;91(14):e00295-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00295-17. Print 2017 Jul 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28468873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jacinto, E., R. Loewith, A. Schmidt, S. Lin, M. A. Rüegg, A. Hall, and M. N. Hall. 2004. Mammalian TOR complex 2 controls the actin cytoskeleton and is rapamycin insensitive. Nat. Cell Biol. 6:1122-1128. - PubMed
-
- Luo, Z., A. K. Saha, X. Xiang, and N. B. Ruderman. 2005. AMPK, the metabolic syndrome and cancer. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 26:69-76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

