Prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype 2 (EP2) regulates microglial activation and associated neurotoxicity induced by aggregated alpha-synuclein
- PMID: 17204153
- PMCID: PMC1766347
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-4-2
Prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype 2 (EP2) regulates microglial activation and associated neurotoxicity induced by aggregated alpha-synuclein
Abstract
Background: The pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson's disease (PD) remains elusive, although evidence has suggested that neuroinflammation characterized by activation of resident microglia in the brain may contribute significantly to neurodegeneration in PD. It has been demonstrated that aggregated alpha-synuclein potently activates microglia and causes neurotoxicity. However, the mechanisms by which aggregated alpha-synuclein activates microglia are not understood fully.
Methods: We investigated the role of prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype 2 (EP2) in alpha-synuclein aggregation-induced microglial activation using ex vivo, in vivo and in vitro experimental systems.
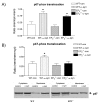
Results: Results demonstrated that ablation of EP2(EP2-/-) significantly enhanced microglia-mediated ex vivo clearance of alpha-synuclein aggregates (from mesocortex of Lewy body disease patients) while significantly attenuating neurotoxicity and extent of alpha-synuclein aggregation in mice treated with a parkinsonian toxicant 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Furthermore, we report that reduced neurotoxicity by EP2-/- microglia could be attributed to suppressed translocation of a critical cytoplasmic subunit (p47-phox) of NADPH oxidase (PHOX) to the membranous compartment after exposure to aggregated alpha-synuclein.
Conclusion: Thus, it appears that microglial EP2 plays a critical role in alpha-synuclein-mediated neurotoxicity.
Figures

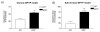
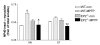
Similar articles
-
Aggregated alpha-synuclein activates microglia: a process leading to disease progression in Parkinson's disease.FASEB J. 2005 Apr;19(6):533-42. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-2751com. FASEB J. 2005. PMID: 15791003
-
Microglial PHOX and Mac-1 are essential to the enhanced dopaminergic neurodegeneration elicited by A30P and A53T mutant alpha-synuclein.Glia. 2007 Aug 15;55(11):1178-88. doi: 10.1002/glia.20532. Glia. 2007. PMID: 17600340
-
FcγRIIB mediates the inhibitory effect of aggregated α-synuclein on microglial phagocytosis.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 Nov;83:90-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.08.025. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 26342897
-
Regulation of α-synuclein homeostasis and inflammasome activation by microglial autophagy.Sci Adv. 2022 Oct 28;8(43):eabn1298. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn1298. Epub 2022 Oct 26. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36288297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Origins and effects of extracellular alpha-synuclein: implications in Parkinson's disease.J Mol Neurosci. 2008;34(1):17-22. doi: 10.1007/s12031-007-0012-9. Epub 2007 Apr 17. J Mol Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18157654 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of WO 2012/177618 A1 and US-2014/0179750 A1: novel small molecule antagonists of prostaglandin-E2 receptor EP2.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015 Jul;25(7):837-44. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2015.1025752. Epub 2015 Mar 15. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015. PMID: 25772215 Free PMC article.
-
Neurons and Glia Interplay in α-Synucleinopathies.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 8;22(9):4994. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094994. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34066733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Perspectives on Roles of Alpha-Synuclein in Parkinson's Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Nov 22;10:370. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00370. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30524265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The prostaglandin E2 E-prostanoid 4 receptor exerts anti-inflammatory effects in brain innate immunity.J Immunol. 2010 Jun 15;184(12):7207-18. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903487. Epub 2010 May 7. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20483760 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-Synuclein, cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandins-EP2 receptors as neuroinflammatory biomarkers of autism spectrum disorders: Use of combined ROC curves to increase their diagnostic values.Lipids Health Dis. 2021 Nov 6;20(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s12944-021-01578-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2021. PMID: 34742290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McGeer PL, Yasojima K, McGeer EG. Inflammation in Parkinson's disease. Adv Neurol. 2001;86:83–89. - PubMed
-
- Kohutnicka M, Lewandowska E, Kurkowska-Jastrzebska I, Czlonkowski A, Czlonkowska A. Microglial and astrocytic involvement in a murine model of Parkinson's disease induced by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) Immunopharmacology. 1998;39:167–180. doi: 10.1016/S0162-3109(98)00022-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

