Nuclear IKK activity leads to dysregulated notch-dependent gene expression in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 17190815
- PMCID: PMC1765449
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0606476104
Nuclear IKK activity leads to dysregulated notch-dependent gene expression in colorectal cancer
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Apr 8;105(14):5650
Abstract
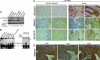
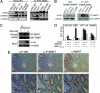
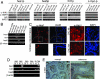
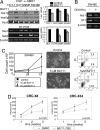
Nuclear functions for IkappaB kinase (IKK), including phosphorylation of histone H3 and nuclear corepressors, have been recently described. Here, we show that IKK is activated in colorectal tumors concomitant with the presence of phosphorylated SMRT (silencing mediator of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptor) corepressor that is aberrantly localized in the cytoplasm. In these tumors, IKKalpha associates to the chromatin of specific Notch targets, leading to the release of SMRT. Abrogation of IKK activity by BAY11-7082 or by expressing dominant negative IKKalpha restores the association of SMRT with Notch target genes, resulting in specific gene repression. Finally, BAY11-7082 significantly reduces tumor size in colorectal cancer xenografts (CRC-Xs) implanted in nude mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
IkappaB kinase alpha-mediated derepression of SMRT potentiates acetylation of RelA/p65 by p300.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Jan;26(2):457-71. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.2.457-471.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16382138 Free PMC article.
-
A truncated form of IKKα is responsible for specific nuclear IKK activity in colorectal cancer.Cell Rep. 2012 Oct 25;2(4):840-54. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.08.028. Epub 2012 Oct 4. Cell Rep. 2012. PMID: 23041317
-
Role of IKK and oscillatory NFkappaB kinetics in MMP-9 gene expression and chemoresistance to 5-fluorouracil in RKO colorectal cancer cells.Mol Carcinog. 2007 May;46(5):402-13. doi: 10.1002/mc.20288. Mol Carcinog. 2007. PMID: 17186550
-
Extending the nuclear roles of IkappaB kinase subunits.Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Oct 30;72(9):1081-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.06.017. Epub 2006 Jul 18. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16846590 Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor-related gene changes in immunosuppressive Syrian hamster cholangiocarcinoma.Pathol Oncol Res. 2013 Oct;19(4):785-94. doi: 10.1007/s12253-013-9645-x. Epub 2013 May 6. Pathol Oncol Res. 2013. PMID: 23645518
-
NF-κB signaling mediates acquired resistance after PARP inhibition.Oncotarget. 2015 Feb 28;6(6):3825-39. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2868. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25686825 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the role of nuclear and cytoplasmic IKKα in skin cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 May 17;7(20):29531-47. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8792. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27121058 Free PMC article.
-
The IκB kinase complex in NF-κB regulation and beyond.EMBO Rep. 2014 Jan;15(1):46-61. doi: 10.1002/embr.201337983. Epub 2013 Dec 27. EMBO Rep. 2014. PMID: 24375677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TBL1 and TBLR1 phosphorylation on regulated gene promoters overcomes dual CtBP and NCoR/SMRT transcriptional repression checkpoints.Mol Cell. 2008 Mar 28;29(6):755-66. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.01.020. Mol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18374649 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW. Trends Genet. 1993;9:138–141. - PubMed
-
- Su LK, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Preisinger AC, Moser AR, Luongo C, Gould KA, Dove WF. Science. 1992;256:668–670. - PubMed
-
- van Es JH, van Gijn ME, Riccio O, van den Born M, Vooijs M, Begthel H, Cozijnsen M, Robine S, Winton DJ, Radtke F, Clevers H. Nature. 2005;435:959–963. - PubMed
-
- Fre S, Huyghe M, Mourikis P, Robine S, Louvard D, Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Nature. 2005;435:964–968. - PubMed
-
- Leong KG, Karsan A. Blood. 2006;107:2223–2233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

