Genome-wide analysis of transcriptional dependence and probable target sites for Abf1 and Rap1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 17158163
- PMCID: PMC1802568
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl1059
Genome-wide analysis of transcriptional dependence and probable target sites for Abf1 and Rap1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
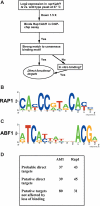
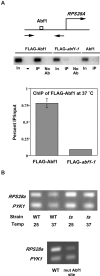
Abf1 and Rap1 are general regulatory factors (GRFs) that contribute to transcriptional activation of a large number of genes, as well as to replication, silencing and telomere structure in yeast. In spite of their widespread roles in transcription, the scope of their functional targets genome-wide has not been previously determined. Here, we use microarrays to examine the contribution of these essential GRFs to transcription genome-wide, by using ts mutants that dissociate from their binding sites at 37 degrees C. We then combine this data with published ChIP-chip studies and motif analysis to identify probable direct targets for Abf1 and Rap1. We also identify a substantial number of genes likely to bind Rap1 or Abf1, but not affected by loss of GRF binding. Interestingly, the results strongly suggest that Rap1 can contribute to gene activation from farther upstream than can Abf1. Also, consistent with previous work, more genes that bind Abf1 are unaffected by loss of binding than those that bind Rap1. Finally, we show for several such genes that the Abf1 C-terminal region, which contains the putative activation domain, is not needed to confer this peculiar 'memory effect' that allows continued transcription after loss of Abf1 binding.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Promoter architecture and transcriptional regulation of Abf1-dependent ribosomal protein genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jul 27;44(13):6113-26. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw194. Epub 2016 Mar 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27016735 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of ABF1 and RAP1 in chromatin opening and transactivator potentiation in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Oct;24(20):9152-64. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.20.9152-9164.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15456886 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of protosilencers in the formation and maintenance of heterochromatin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37092. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037092. Epub 2012 May 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22615905 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple roles of the general regulatory factor Abf1 in yeast ribosome biogenesis.Curr Genet. 2017 Feb;63(1):65-68. doi: 10.1007/s00294-016-0621-3. Epub 2016 Jun 4. Curr Genet. 2017. PMID: 27262581 Review.
-
The multifunctional transcription factor Rap1: a regulator of yeast physiology.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016 Jun 1;21(5):918-30. doi: 10.2741/4429. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016. PMID: 27100480 Review.
Cited by
-
Abf1 Is an Essential Protein That Participates in Cell Cycle Progression and Subtelomeric Silencing in Candida glabrata.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Nov 25;7(12):1005. doi: 10.3390/jof7121005. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34946988 Free PMC article.
-
Promoter architecture and transcriptional regulation of Abf1-dependent ribosomal protein genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jul 27;44(13):6113-26. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw194. Epub 2016 Mar 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27016735 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-scale study of the importance of binding site context for transcription factor binding and gene regulation.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Nov 17;9:484. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-484. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 19014636 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary divergence of intrinsic and trans-regulated nucleosome positioning sequences reveals plastic rules for chromatin organization.Genome Res. 2011 Nov;21(11):1851-62. doi: 10.1101/gr.122267.111. Epub 2011 Sep 13. Genome Res. 2011. PMID: 21914852 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide expression profiling, in vivo DNA binding analysis, and probabilistic motif prediction reveal novel Abf1 target genes during fermentation, respiration, and sporulation in yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 May;19(5):2193-207. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-12-1242. Epub 2008 Feb 27. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18305101 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morse R.H. RAP, RAP, open up! new wrinkles for RAP1 in yeast. Trends Genet. 2000;16:51–53. - PubMed
-
- Shore D. RAP1: a protean regulator in yeast. Trends Genet. 1994;10:408–412. - PubMed
-
- Lee T.I., Rinaldi N.J., Robert F., Odom D.T., Bar-Joseph Z., Gerber G.K., Hannett N.M., Harbison C.T., Thompson C.M., Simon I., et al. Transcriptional regulatory networks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 2002;298:799–804. - PubMed
-
- Lieb J.D., Liu X., Botstein D., Brown P.O. Promoter-specific binding of Rap1 revealed by genome-wide maps of protein–DNA association. Nature Genet. 2001;28:327–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

