HLA-DM targets the hydrogen bond between the histidine at position beta81 and peptide to dissociate HLA-DR-peptide complexes
- PMID: 17143275
- PMCID: PMC3019572
- DOI: 10.1038/ni1414
HLA-DM targets the hydrogen bond between the histidine at position beta81 and peptide to dissociate HLA-DR-peptide complexes
Abstract
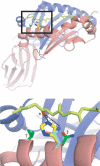
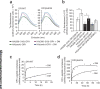
The peptide editor HLA-DM (DM) mediates exchange of peptides bound to major histocompatibility (MHC) class II molecules during antigen processing; however, the mechanism by which DM displaces peptides remains unclear. Here we generated a soluble mutant HLA-DR1 with a histidine-to-asparagine substitution at position 81 of the beta-chain (DR1betaH81N) to perturb an important hydrogen bond between MHC class II and peptide. Peptide-DR1betaH81N complexes dissociated at rates similar to the dissociation rates of DM-induced peptide-wild-type DR1, and DM did not enhance the dissociation of peptide-DR1betaH81N complexes. Reintroduction of an appropriate hydrogen bond (DR1betaH81N betaV85H) restored DM-mediated peptide dissociation. Thus, DR1betaH81N might represent a 'post-DM effect' conformation. We suggest that DM may mediate peptide dissociation by a 'hit-and-run' mechanism that results in conformational changes in MHC class II molecules and disruption of hydrogen bonds between betaHis81 and bound peptide.
Figures
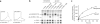
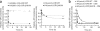
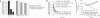
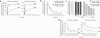
Similar articles
-
Cutting edge: HLA-DM functions through a mechanism that does not require specific conserved hydrogen bonds in class II MHC-peptide complexes.J Immunol. 2009 Oct 1;183(7):4187-91. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901663. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19767569 Free PMC article.
-
Editing of the HLA-DR-peptide repertoire by HLA-DM.EMBO J. 1996 Nov 15;15(22):6144-54. EMBO J. 1996. PMID: 8947036 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of histidine beta81 of HLA-DR101 on peptide binding and presentation to T-cell receptor.Hum Immunol. 2002 Jun;63(6):459-66. doi: 10.1016/s0198-8859(02)00394-4. Hum Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12039521
-
Conformational variation in structures of classical and non-classical MHCII proteins and functional implications.Immunol Rev. 2012 Nov;250(1):144-57. doi: 10.1111/imr.12003. Immunol Rev. 2012. PMID: 23046127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How HLA-DM affects the peptide repertoire bound to HLA-DR molecules.Hum Immunol. 1997 May;54(2):170-9. doi: 10.1016/s0198-8859(97)00077-3. Hum Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9297535 Review.
Cited by
-
Human Hepatitis B Viral Infection Outcomes Are Linked to Naturally Occurring Variants of HLA-DOA That Have Altered Function.J Immunol. 2020 Aug 15;205(4):923-935. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000476. Epub 2020 Jul 20. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32690655 Free PMC article.
-
The Thermodynamic Mechanism of Peptide-MHC Class II Complex Formation Is a Determinant of Susceptibility to HLA-DM.J Immunol. 2015 Aug 1;195(3):1251-61. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402367. Epub 2015 Jun 26. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26116504 Free PMC article.
-
HLA-DM: arbiter conformationis.Immunology. 2013 Feb;138(2):85-92. doi: 10.1111/imm.12030. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 23113687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The control of the specificity of CD4 T cell responses: thresholds, breakpoints, and ceilings.Front Immunol. 2013 Oct 23;4:340. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00340. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24167504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Insights Into HLA-DM Mediated MHC II Peptide Exchange.Curr Top Biochem Res. 2011;13(2):39-55. Curr Top Biochem Res. 2011. PMID: 25264402 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neefjes JJ, Stollorz V, Peters PJ, Geuze HJ, Ploegh HL. The biosynthetic pathway of MHC class II but not class I molecules intersects the endocytic route. Cell. 1990;61:171–183. - PubMed
-
- Peters PJ, Neefjes JJ, Oorschot V, Ploegh HL, Geuze HJ. Segregation of MHC class II molecules from MHC class I molecules in the Golgi complex for transport to lysosomal compartments. Nature. 1991;349:669–676. - PubMed
-
- Cresswell P. Assembly, transport, and function of MHC class II molecules. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1994;12:259–293. - PubMed
-
- Sadegh-Nasseri S, McConnell HM. A kinetic intermediate in the reaction of an antigenic peptide and I-Ek. Nature. 1989;337:274–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

