Release probability-dependent scaling of the postsynaptic responses at single hippocampal GABAergic synapses
- PMID: 17135411
- PMCID: PMC2630420
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3106-06.2006
Release probability-dependent scaling of the postsynaptic responses at single hippocampal GABAergic synapses
Abstract
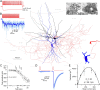
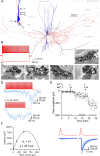
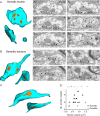
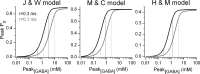
The amount of neurotransmitter released after the arrival of an action potential affects the strength and the trial-to-trial variability of postsynaptic responses. Most studies examining the dependence of synaptic neurotransmitter concentration on the release probability (P(r)) have focused on glutamatergic synapses. Here we asked whether univesicular or multivesicular release characterizes transmission at hippocampal GABAergic synapses. We used multiple probability functional analysis to derive quantal parameters at inhibitory connections between cannabinoid receptor- and cholecystokinin (CCK)-expressing interneurons and CA3 pyramidal cells. After the recordings, the cells were visualized and reconstructed at the light-microscopic level, and the number of boutons mediating the IPSCs was determined using electron microscopy (EM). The number of active zones (AZs) per CCK-immunopositive bouton was determined from three-dimensional EM reconstructions, thus allowing the calculation of the total number of AZs for each pair. Our results reveal an approximate fivefold discrepancy between the numbers of functionally determined release sites (17.4 +/- 3.2) and structurally identified AZs (3.7 +/- 0.9). Channel modeling predicts that a fivefold to sevenfold increase in the peak synaptic GABA concentration is required for the fivefold enhancement of the postsynaptic responses. Kinetic analysis of the unitary IPSCs indicates that the increase in synaptic GABA concentration is most likely attributable to multivesicular release. This change in the synaptic GABA concentration transient together with extremely low postsynaptic receptor occupancy permits a P(r)-dependent scaling of the postsynaptic response generated at a single hippocampal GABAergic synaptic contact.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Target Cell Type-Dependent Differences in Ca2+ Channel Function Underlie Distinct Release Probabilities at Hippocampal Glutamatergic Terminals.J Neurosci. 2017 Feb 15;37(7):1910-1924. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2024-16.2017. Epub 2017 Jan 23. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28115484 Free PMC article.
-
Quantal size is independent of the release probability at hippocampal excitatory synapses.J Neurosci. 2005 Jan 5;25(1):223-32. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3688-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15634785 Free PMC article.
-
GABA B receptor modulation of excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission onto rat CA3 hippocampal interneurons.J Physiol. 2003 Jan 15;546(Pt 2):439-53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.034017. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12527730 Free PMC article.
-
The synaptic split of SNAP-25: different roles in glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons?Neuroscience. 2009 Jan 12;158(1):223-30. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.03.014. Epub 2008 Mar 20. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 18514426 Review. No abstract available.
-
Synaptic inhibition and γ-aminobutyric acid in the mammalian central nervous system.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2013;89(4):139-56. doi: 10.2183/pjab.89.139. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23574805 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Presynaptic inhibitory terminals are functionally abnormal in a rat model of posttraumatic epilepsy.J Neurophysiol. 2010 Jul;104(1):280-90. doi: 10.1152/jn.00351.2010. Epub 2010 May 19. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20484536 Free PMC article.
-
Plasticity of GABA transporters: an unconventional route to shape inhibitory synaptic transmission.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 May 13;8:128. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00128. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24860430 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic ribbons influence the size and frequency of miniature-like evoked postsynaptic currents.Neuron. 2013 Feb 6;77(3):516-27. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.11.024. Neuron. 2013. PMID: 23395377 Free PMC article.
-
Variability in the Munc13-1 content of excitatory release sites.Elife. 2021 Apr 27;10:e67468. doi: 10.7554/eLife.67468. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33904397 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic Protein Synthesis Is Required for Long-Term Plasticity of GABA Release.Neuron. 2016 Oct 19;92(2):479-492. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.09.040. Neuron. 2016. PMID: 27764673 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott LF, Regehr WG. Synaptic computation. Nature. 2004;431:796–803. - PubMed
-
- Auger C, Marty A. Heterogeneity of functional synaptic parameters among single release sites. Neuron. 1997;19:139–150. - PubMed
-
- Bergles DE, Diamond JS, Jahr CE. Clearance of glutamate inside the synapse and beyond. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1999;9:293–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
