Immunosuppressive strategies that are mediated by tumor cells
- PMID: 17134371
- PMCID: PMC2895922
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141609
Immunosuppressive strategies that are mediated by tumor cells
Abstract
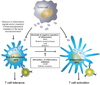
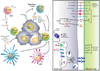
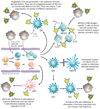
Despite major advances in understanding the mechanisms leading to tumor immunity, a number of obstacles hinder the successful translation of mechanistic insights into effective tumor immunotherapy. Such obstacles include the ability of tumors to foster a tolerant microenvironment and the activation of a plethora of immunosuppressive mechanisms, which may act in concert to counteract effective immune responses. Here we discuss different strategies employed by tumors to thwart immune responses, including tumor-induced impairment of antigen presentation, the activation of negative costimulatory signals, and the elaboration of immunosuppressive factors. In addition, we underscore the influence of regulatory cell populations that may contribute to this immunosuppressive network; these include regulatory T cells, natural killer T cells, and distinct subsets of immature and mature dendritic cells. The current wealth of preclinical information promises a future scenario in which the synchronized blockade of immunosuppressive mechanisms may be effective in combination with other conventional strategies to overcome immunological tolerance and promote tumor regression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor gangliosides and T cells: a deadly encounter.Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4(2):502-19. doi: 10.2741/s281. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2012. PMID: 22202073 Review.
-
Breaking immunotolerance of tumors: a new perspective for dendritic cell therapy.J Immunotoxicol. 2014 Oct;11(4):311-8. doi: 10.3109/1547691X.2013.865094. Epub 2014 Feb 4. J Immunotoxicol. 2014. PMID: 24495309 Review.
-
Regulatory T cell: a protection for tumour cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2012 Mar;16(3):425-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01437.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 21895966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-host immune interactions and dendritic cell dysfunction.Adv Cancer Res. 2004;92:13-27. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(04)92002-7. Adv Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15530555 Review.
-
Immune evasion in cancer: Mechanistic basis and therapeutic strategies.Semin Cancer Biol. 2015 Dec;35 Suppl:S185-S198. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.03.004. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Semin Cancer Biol. 2015. PMID: 25818339 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of extracellular vesicle uptake and implications for the design of cancer therapeutics.J Extracell Biol. 2024 Oct 30;3(11):e70017. doi: 10.1002/jex2.70017. eCollection 2024 Nov. J Extracell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39483807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The combination of a low-dose chemotherapeutic agent, 5-fluorouracil, and an adenoviral tumor vaccine has a synergistic benefit on survival in a tumor model system.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 28;8(6):e67904. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067904. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23840786 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review on the role of the gut microbiota in tumors and their treatment.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 8;15:1355387. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1355387. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39175566 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies for enhancing vaccine-induced CTL antitumor immune responses.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:605045. doi: 10.1155/2012/605045. Epub 2012 Oct 2. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 23093850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of LRP5 and LRP6 in dendritic cells enhances antitumor immunity.Oncoimmunology. 2015 Dec 14;5(4):e1115941. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2015.1115941. eCollection 2016 Apr. Oncoimmunology. 2015. PMID: 27141399 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smyth MJ, Godfrey DI, Trapani JA. A fresh look at tumor immunosurveillance and immunotherapy. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:293–299. - PubMed
-
- Drake CG, Jaffee E, Pardoll DM. Mechanisms of immune evasion by tumors. Adv Immunol. 2006;90:51–81. - PubMed
-
- Dunn GP, Old LJ, Schreiber RD. The three Es of cancer immunoediting. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:329–360. - PubMed
-
- Shankaran V, Ikeda H, Bruce AT, White JM, Swanson PE, Old LJ, Schreiber RD. IFN-γ and lymphocytes prevent primary tumor development and shape tumor immunogenicity. Nature. 2001;410:1107–1111. - PubMed
-
- Boon T, Coulie PG, Van den Eynde BJ, Van der Bruggen P. Human T-cell responses against melanoma. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:175–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

