Chromatin structure can strongly facilitate enhancer action over a distance
- PMID: 17101994
- PMCID: PMC1693808
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0603819103
Chromatin structure can strongly facilitate enhancer action over a distance
Abstract
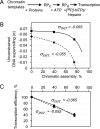
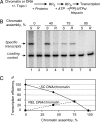
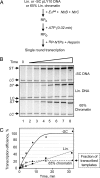
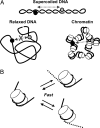
Numerous DNA transactions in eukaryotic nuclei are regulated by elements (enhancers) that can directly interact with their targets over large regions of DNA organized into chromatin. The mechanisms allowing communication over a distance in chromatin are unknown. We have established an experimental system allowing quantitative analysis of the impact of chromatin structure on distant transcriptional regulation. Assembly of relaxed or linear DNA templates into subsaturated chromatin results in a strong increase of the efficiency of distant enhancer-promoter E-P communication and activation of transcription. The effect is directly proportional to the efficiency of chromatin assembly and cannot be explained only by DNA compaction. Transcription activation on chromatin templates is enhancer- and activator-dependent, and must be accompanied by direct E-P interaction and formation of a chromatin loop. Previously we have shown that DNA supercoiling can strongly facilitate E-P communication on histone-free DNA. The effects of chromatin assembly and DNA supercoiling on the communication are quantitatively similar, but the efficiency of enhancer action in subsaturated chromatin does not depend on the level of unconstrained DNA supercoiling. Thus chromatin structure per se can support highly efficient communication over a distance and functionally mimic the supercoiled state characteristic for prokaryotic DNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rationally designed insulator-like elements can block enhancer action in vitro.EMBO J. 2003 Sep 15;22(18):4728-37. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg468. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12970185 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical analysis of enhancer-promoter communication in chromatin.Methods. 2007 Mar;41(3):250-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2006.11.003. Methods. 2007. PMID: 17309834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Mechanisms of distant enhancer action on DNA and in chromatin].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2009 Mar-Apr;43(2):204-14. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2009. PMID: 19425490 Review. Russian.
-
The effect of the DNA conformation on the rate of NtrC activated transcription of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase.sigma(54) holoenzyme.J Mol Biol. 2000 Jul 21;300(4):709-25. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3921. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10891265
-
Communication over a large distance: enhancers and insulators.Biochem Cell Biol. 2003 Jun;81(3):241-51. doi: 10.1139/o03-051. Biochem Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12897858 Review.
Cited by
-
Internucleosomal interactions mediated by histone tails allow distant communication in chromatin.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 8;287(24):20248-57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.333104. Epub 2012 Apr 19. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22518845 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for heteromorphic chromatin fibers from analysis of nucleosome interactions.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Aug 11;106(32):13317-22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0903280106. Epub 2009 Jul 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19651606 Free PMC article.
-
Micro- and nanofluidic technologies for epigenetic profiling.Biomicrofluidics. 2013 Jul 24;7(4):41301. doi: 10.1063/1.4816835. eCollection 2013 Jul. Biomicrofluidics. 2013. PMID: 23964309 Free PMC article.
-
GeneHancer: genome-wide integration of enhancers and target genes in GeneCards.Database (Oxford). 2017 Jan 1;2017:bax028. doi: 10.1093/database/bax028. Database (Oxford). 2017. PMID: 28605766 Free PMC article.
-
[Opposite Effects of Histone H1 and HMGN5 Protein on Distant Interactions in Chromatin].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2019 Nov-Dec;53(6):1038-1048. doi: 10.1134/S0026898419060132. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2019. PMID: 31876282 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

