Global mapping of c-Myc binding sites and target gene networks in human B cells
- PMID: 17093053
- PMCID: PMC1635161
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0604129103
Global mapping of c-Myc binding sites and target gene networks in human B cells
Abstract
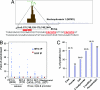
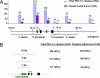
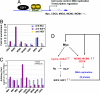
The protooncogene MYC encodes the c-Myc transcription factor that regulates cell growth, cell proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis. Although deregulation of MYC contributes to tumorigenesis, it is still unclear what direct Myc-induced transcriptomes promote cell transformation. Here we provide a snapshot of genome-wide, unbiased characterization of direct Myc binding targets in a model of human B lymphoid tumor using ChIP coupled with pair-end ditag sequencing analysis (ChIP-PET). Myc potentially occupies > 4,000 genomic loci with the majority near proximal promoter regions associated frequently with CpG islands. Using gene expression profiles with ChIP-PET, we identified 668 direct Myc-regulated gene targets, including 48 transcription factors, indicating that Myc is a central transcriptional hub in growth and proliferation control. This first global genomic view of Myc binding sites yields insights of transcriptional circuitries and cis regulatory modules involving Myc and provides a substantial framework for our understanding of mechanisms of Myc-induced tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-wide analysis of c-MYC-regulated mRNAs and miRNAs, and c-MYC DNA binding by next-generation sequencing.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1012:145-85. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-429-6_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 24006064
-
Genomic targets of the human c-Myc protein.Genes Dev. 2003 May 1;17(9):1115-29. doi: 10.1101/gad.1067003. Epub 2003 Apr 14. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 12695333 Free PMC article.
-
A global map of p53 transcription-factor binding sites in the human genome.Cell. 2006 Jan 13;124(1):207-19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.10.043. Cell. 2006. PMID: 16413492
-
Making myc.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006;302:1-32. doi: 10.1007/3-540-32952-8_1. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16620023 Review.
-
MYC and the art of microRNA maintenance.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014 Apr 15;4(8):a014175. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a014175. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014. PMID: 24737842 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction with WDR5 promotes target gene recognition and tumorigenesis by MYC.Mol Cell. 2015 May 7;58(3):440-52. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.02.028. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25818646 Free PMC article.
-
Amplitude modulation of androgen signaling by c-MYC.Genes Dev. 2013 Apr 1;27(7):734-48. doi: 10.1101/gad.209569.112. Epub 2013 Mar 25. Genes Dev. 2013. PMID: 23530127 Free PMC article.
-
IL-21 Stimulates the expression and activation of cell cycle regulators and promotes cell proliferation in EBV-positive diffuse large B cell lymphoma.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 23;10(1):12326. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69227-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32704112 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Function Of The Tumor Suppressor BRCA1.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2012 Apr 1;1(1):e201204005. doi: 10.5936/csbj.201204005. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2012. PMID: 22737296 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming of proline and glutamine metabolism contributes to the proliferative and metabolic responses regulated by oncogenic transcription factor c-MYC.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jun 5;109(23):8983-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203244109. Epub 2012 May 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22615405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adhikary S, Eilers M. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:635–645. - PubMed
-
- Grandori C, Cowley SM, James LP, Eisenman RN. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2000;16:653–699. - PubMed
-
- Blackwood EM, Eisenman RN. Science. 1991;251:1211–1217. - PubMed
-
- Claassen GF, Hann SR. Oncogene. 1999;18:2925–2933. - PubMed
-
- Amati B, Brooks MW, Levy N, Littlewood TD, Evan GI, Land H. Cell. 1993;72:233–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

