Catenins: keeping cells from getting their signals crossed
- PMID: 17084354
- PMCID: PMC2405914
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.10.010
Catenins: keeping cells from getting their signals crossed
Abstract
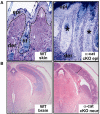
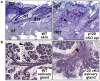
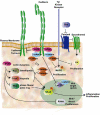
Adherens junctions have been traditionally viewed as building blocks of tissue architecture. The foundations for this view began to change with the discovery that a central component of AJs, beta-catenin, can also function as a transcriptional cofactor in Wnt signaling. In recent years, conventional views have similarly been shaken about the other two major AJ catenins, alpha-catenin and p120-catenin. Catenins have emerged as molecular sensors that integrate cell-cell junctions and cytoskeletal dynamics with signaling pathways that govern morphogenesis, tissue homeostasis, and even intercellular communication between different cell types within a tissue. These findings reveal novel aspects of AJ function in normal tissues and offer insights into how changes in AJs and their associated proteins and cytoskeletal dynamics impact wound-repair and cancer.
Figures
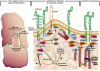

Similar articles
-
Signaling from adherens-type junctions.Eur J Cell Biol. 2005 Mar;84(2-3):235-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2004.12.007. Eur J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15819404 Review. No abstract available.
-
Is the cadherin/catenin complex a functional unit of cell-cell actin-based adherens junctions in the rat testis?Biol Reprod. 2003 Feb;68(2):489-508. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.102.005793. Biol Reprod. 2003. PMID: 12533412
-
Regulation of the assembly and adhesion activity of E-cadherin by nectin and afadin for the formation of adherens junctions in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells.J Biol Chem. 2006 Feb 24;281(8):5288-99. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510070200. Epub 2005 Dec 18. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16361708
-
[Structure and function of cadherin-catenin complex].Seikagaku. 2006 Jul;78(7):579-87. Seikagaku. 2006. PMID: 16910550 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Rho1 regulates Drosophila adherens junctions independently of p120ctn.Development. 2005 Nov;132(21):4819-31. doi: 10.1242/dev.02056. Epub 2005 Oct 5. Development. 2005. PMID: 16207756
Cited by
-
Biological influence of Hakai in cancer: a 10-year review.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012 Jun;31(1-2):375-86. doi: 10.1007/s10555-012-9348-x. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012. PMID: 22349934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of E-cadherin-mediated adhesion induces a functionally distinct pathway of dendritic cell maturation.Immunity. 2007 Oct;27(4):610-24. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.08.015. Epub 2007 Oct 11. Immunity. 2007. PMID: 17936032 Free PMC article.
-
α-Catenin inhibits glioma cell migration, invasion, and proliferation by suppression of β-catenin transactivation.J Neurooncol. 2011 Jul;103(3):445-51. doi: 10.1007/s11060-010-0413-4. Epub 2010 Sep 26. J Neurooncol. 2011. PMID: 20872274
-
Loss of function of e-cadherin in embryonic stem cells and the relevance to models of tumorigenesis.J Oncol. 2011;2011:352616. doi: 10.1155/2011/352616. Epub 2010 Dec 9. J Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21197469 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic ablation of alphav integrins in epithelial cells of the eyelid skin and conjunctiva leads to squamous cell carcinoma.Am J Pathol. 2008 Jun;172(6):1740-7. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070700. Epub 2008 May 8. Am J Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18467691 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

