Dimeric Eg5 maintains processivity through alternating-site catalysis with rate-limiting ATP hydrolysis
- PMID: 17062577
- PMCID: PMC1866285
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M608056200
Dimeric Eg5 maintains processivity through alternating-site catalysis with rate-limiting ATP hydrolysis
Abstract
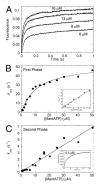
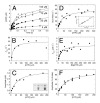
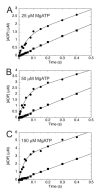
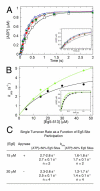
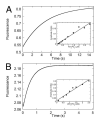
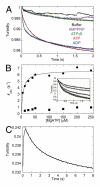
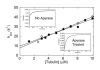
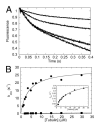
Eg5/KSP is a homotetrameric, Kinesin-5 family member whose ability to cross-link microtubules has associated it with mitotic spindle assembly and dynamics for chromosome segregation. Transient-state kinetic methodologies have been used to dissect the mechanochemical cycle of a dimeric motor, Eg5-513, to better understand the cooperative interactions that modulate processive stepping. Microtubule association, ADP release, and ATP binding are all fast steps in the pathway. However, the acid-quench analysis of the kinetics of ATP hydrolysis with substrate in excess of motor was unable to resolve a burst of product formation during the first turnover event. In addition, the kinetics of P(i) release and ATP-promoted microtubule-Eg5 dissociation were observed to be no faster than the rate of ATP hydrolysis. In combination the data suggest that dimeric Eg5 is the first kinesin motor identified to have a rate-limiting ATP hydrolysis step. Furthermore, several lines of evidence implicate alternating-site catalysis as the molecular mechanism underlying dimeric Eg5 processivity. Both mantATP binding and mantADP release transients are biphasic. Analysis of ATP hydrolysis through single turnover assays indicates a surprising substrate concentration dependence, where the observed rate is reduced by half when substrate concentration is sufficiently high to require both motor domains of the dimer to participate in the reaction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
To step or not to step? How biochemistry and mechanics influence processivity in Kinesin and Eg5.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007 Feb;19(1):75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2006.12.011. Epub 2006 Dec 26. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17188855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Getting in sync with dimeric Eg5. Initiation and regulation of the processive run.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jan 25;283(4):2078-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M708354200. Epub 2007 Nov 25. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18037705 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic analysis of the mitotic kinesin Eg5.J Biol Chem. 2004 Sep 10;279(37):38861-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404203200. Epub 2004 Jul 6. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15247293 Free PMC article.
-
Monastrol inhibition of the mitotic kinesin Eg5.J Biol Chem. 2005 Apr 1;280(13):12658-67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413140200. Epub 2005 Jan 23. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15665380 Free PMC article.
-
The kinetic mechanism of kinesin.Trends Biochem Sci. 2004 Jun;29(6):301-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2004.04.010. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004. PMID: 15276184 Review.
Cited by
-
To step or not to step? How biochemistry and mechanics influence processivity in Kinesin and Eg5.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007 Feb;19(1):75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2006.12.011. Epub 2006 Dec 26. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17188855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kinesin-5: cross-bridging mechanism to targeted clinical therapy.Gene. 2013 Dec 1;531(2):133-49. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.08.004. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23954229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NSC 622124 inhibits human Eg5 and other kinesins via interaction with the conserved microtubule-binding site.Biochemistry. 2009 Mar 3;48(8):1754-62. doi: 10.1021/bi801291q. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19236100 Free PMC article.
-
The structural kinetics of switch-1 and the neck linker explain the functions of kinesin-1 and Eg5.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Dec 1;112(48):E6606-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1512305112. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26627252 Free PMC article.
-
The Kinesin-5 Chemomechanical Cycle Is Dominated by a Two-heads-bound State.J Biol Chem. 2016 Sep 23;291(39):20283-20294. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.730697. Epub 2016 Jul 11. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27402829 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

