Dicer-derived microRNAs are utilized by the fragile X mental retardation protein for assembly on target RNAs
- PMID: 17057366
- PMCID: PMC1698263
- DOI: 10.1155/JBB/2006/64347
Dicer-derived microRNAs are utilized by the fragile X mental retardation protein for assembly on target RNAs
Abstract
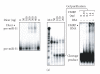
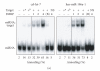
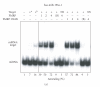
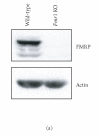
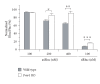
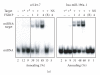
In mammalian cells, fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP) has been reported to be part of a microRNA (miRNA)-containing effector ribonucleoprotien (RNP) complex believed to mediate translational control of specific mRNAs. Here, using recombinant proteins, we demonstrate that human FMRP can act as a miRNA acceptor protein for the ribonuclease Dicer and facilitate the assembly of miRNAs on specific target RNA sequences. The miRNA assembler property of FMRP was abrogated upon deletion of its single-stranded (ss) RNA binding K-homology domains. The requirement of FMRP for efficient RNA interference (RNAi) in vivo was unveiled by reporter gene silencing assays using various small RNA inducers, which also supports its involvement in an ss small interfering RNA (siRNA)-containing RNP (siRNP) effector complex in mammalian cells. Our results define a possible role for FMRP in RNA silencing and may provide further insight into the molecular defects in patients with the fragile X syndrome.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Hypothesis: a role for fragile X mental retardation protein in mediating and relieving microRNA-guided translational repression?J Biomed Biotechnol. 2006;2006(4):16806. doi: 10.1155/JBB/2006/16806. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 17057359 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of messenger RNAs and microRNAs associated with fragile X mental retardation protein.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;342:267-76. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-123-1:267. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16957381 Review.
-
Kissing complex RNAs mediate interaction between the Fragile-X mental retardation protein KH2 domain and brain polyribosomes.Genes Dev. 2005 Apr 15;19(8):903-18. doi: 10.1101/gad.1276805. Epub 2005 Apr 1. Genes Dev. 2005. PMID: 15805463 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and genetic interaction between the fragile X mental retardation protein and the microRNA pathway.Nat Neurosci. 2004 Feb;7(2):113-7. doi: 10.1038/nn1174. Epub 2004 Jan 4. Nat Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 14703574
-
RNA interference: a new mechanism by which FMRP acts in the normal brain? What can Drosophila teach us?Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2004;10(1):68-74. doi: 10.1002/mrdd.20011. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2004. PMID: 14994291 Review.
Cited by
-
Fragile X syndrome: an update on developing treatment modalities.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2011 Aug 17;2(8):402-10. doi: 10.1021/cn200019z. Epub 2011 Mar 22. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22860169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of synaptic structure and function by FMRP-associated microRNAs miR-125b and miR-132.Neuron. 2010 Feb 11;65(3):373-84. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.01.005. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 20159450 Free PMC article.
-
Gene regulation by non-coding RNAs.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2014 Jan-Feb;49(1):16-32. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2013.844092. Epub 2013 Oct 28. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24164576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics, microRNA, and addiction.Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2014 Sep;16(3):335-44. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2014.16.3/pkenny. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25364284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of human Dicer by the resident ER membrane protein CLIMP-63.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Dec;40(22):11603-17. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks903. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 23047949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–297. - PubMed
-
- Lee Y, Ahn C, Han J, et al. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature. 2003;425(6956):415–419. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature. 2001;409(6818):363–366. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

