Human cytomegalovirus IE86 attenuates virus- and tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced NFkappaB-dependent gene expression
- PMID: 17041226
- PMCID: PMC1641772
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01195-06
Human cytomegalovirus IE86 attenuates virus- and tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced NFkappaB-dependent gene expression
Abstract
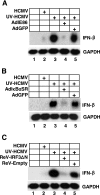
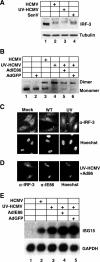
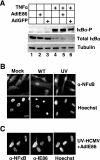
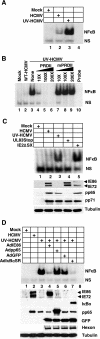
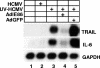
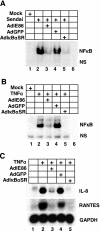
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection regulates a number of genes involved in the host antiviral response. We have previously reported that HCMV attenuates the expression of beta interferon (IFN-beta) and a number of proinflammatory chemokines, and this attenuation is mediated by the HCMV immediate-early protein IE86. The present study seeks to identify the mechanism by which IE86 blocks IFN-beta expression. We demonstrate that the induction of IFN-beta during HCMV infection requires the activation of both the IRF-3 and the NFkappaB pathways. Therefore, IE86 may target either pathway to block IFN-beta expression. Our results show that IE86 does not block IRF-3 phosphorylation, dimerization, nuclear translocation, or target gene expression. However, using gel shift analysis, we demonstrate that IE86 efficiently inhibits virus-induced binding of NFkappaB to the IFN-beta promoter, resulting in attenuation of IFN-beta and NFkappaB-dependent gene expression. Furthermore, IE86 expression inhibits tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced NFkappaB DNA binding and target gene expression. Together, these results identify IE86 as a NFkappaB antagonist, which results in the suppression of NFkappaB-dependent cytokine and chemokine gene expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human cytomegalovirus immediate-early 2 gene expression blocks virus-induced beta interferon production.J Virol. 2005 Mar;79(6):3873-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.6.3873-3877.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15731283 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus immediate-early 2 protein IE86 blocks virus-induced chemokine expression.J Virol. 2006 Jan;80(2):920-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.2.920-928.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16378994 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kappaB-mediated activation of the chemokine CCL22 by the product of the human cytomegalovirus gene UL144 escapes regulation by viral IE86.J Virol. 2008 May;82(9):4250-6. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02156-07. Epub 2008 Feb 20. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18287226 Free PMC article.
-
Functional roles of the human cytomegalovirus essential IE86 protein.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;325:133-52. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-77349-8_8. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18637504 Review.
-
Multifaceted evasion of the interferon response by cytomegalovirus.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009 Sep;29(9):609-19. doi: 10.1089/jir.2009.0064. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009. PMID: 19708810 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epstein-Barr virus BGLF4 kinase downregulates NF-κB transactivation through phosphorylation of coactivator UXT.J Virol. 2012 Nov;86(22):12176-86. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01918-12. Epub 2012 Aug 29. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22933289 Free PMC article.
-
HCMV-encoded US7 and US8 act as antagonists of innate immunity by distinctively targeting TLR-signaling pathways.Nat Commun. 2019 Oct 11;10(1):4670. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12641-4. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31604943 Free PMC article.
-
The IκB Kinases Restrict Human Cytomegalovirus Infection.J Virol. 2019 Apr 17;93(9):e02030-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02030-18. Print 2019 May 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30760575 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse mechanisms evolved by DNA viruses to inhibit early host defenses.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Nov/Dec;51(6):452-481. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2016.1226250. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27650455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-like receptor sensing of human herpesvirus infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012 Oct 8;2:122. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00122. eCollection 2012. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23061052 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agalioti, T., S. Lomvardas, B. Parekh, J. Yie, T. Maniatis, and D. Thanos. 2000. Ordered recruitment of chromatin modifying and general transcription factors to the IFN-beta promoter. Cell 103:667-678. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal, B. B., G. Sethi, A. Nair, and H. Ichikawa. 2006. Nuclear factor-{kappa}B: a holy grail in cancer prevention and therapy. Curr. Signal Transduct. Ther. 1:25-52.
-
- Alcami, A. 2003. Viral mimicry of cytokines, chemokines and their receptors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3:36-50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

