Different mechanisms exist for the plasticity of glutamate reuptake during early long-term potentiation (LTP) and late LTP
- PMID: 17035530
- PMCID: PMC6674676
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2579-06.2006
Different mechanisms exist for the plasticity of glutamate reuptake during early long-term potentiation (LTP) and late LTP
Abstract
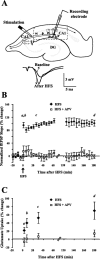
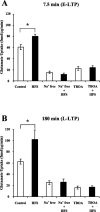
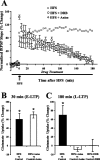
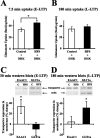
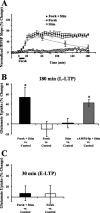
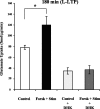
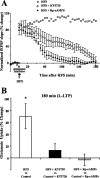
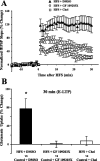
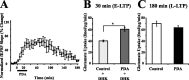
Regulation of glutamate reuptake occurs along with several forms of synaptic plasticity. These associations led to the hypothesis that regulation of glutamate uptake is a general component of plasticity at glutamatergic synapses. We tested this hypothesis by determining whether glutamate uptake is regulated during both the early phases (E-LTP) and late phases (L-LTP) of long-term potentiation (LTP). We found that glutamate uptake was rapidly increased within minutes after induction of LTP and that the increase in glutamate uptake persisted for at least 3 h in CA1 of the hippocampus. NMDA receptor activation and Na+-dependent high-affinity glutamate transporters were responsible for the regulation of glutamate uptake during all phases of LTP. However, different mechanisms appear to be responsible for the increase in glutamate uptake during E-LTP and L-LTP. The increase in glutamate uptake observed during E-LTP did not require new protein synthesis, was mediated by PKC but not cAMP, and as previously shown was attributable to EAAC1 (excitatory amino acid carrier-1), a neuronal glutamate transporter. On the other hand, the increase in glutamate uptake during L-LTP required new protein synthesis and was mediated by the cAMP-PKA (protein kinase A) pathway, and it involved a different glutamate transporter, GLT1a (glutamate transporter subtype 1a). The switch in mechanisms regulating glutamate uptake between E-LTP and L-LTP paralleled the differences in the mechanisms responsible for the induction of E-LTP and L-LTP. Moreover, the differences in signaling pathways and transporters involved in regulating glutamate uptake during E-LTP and L-LTP indicate that different functions and/or sites may exist for the changes in glutamate uptake during E-LTP and L-LTP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationship between increase in astrocytic GLT-1 glutamate transport and late-LTP.Learn Mem. 2012 Nov 19;19(12):615-26. doi: 10.1101/lm.023259.111. Learn Mem. 2012. PMID: 23166293 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the anoxia-induced long-term synaptic potentiation in area CA1 of the rat hippocampus.Br J Pharmacol. 1997 Oct;122(4):671-81. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701409. Br J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9375963 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term potentiation and contextual fear conditioning increase neuronal glutamate uptake.Nat Neurosci. 2002 Feb;5(2):155-61. doi: 10.1038/nn791. Nat Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11788834
-
LTD, LTP, and the sliding threshold for long-term synaptic plasticity.Hippocampus. 1996;6(1):35-42. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1063(1996)6:1<35::AID-HIPO7>3.0.CO;2-6. Hippocampus. 1996. PMID: 8878740 Review.
-
Presynaptic mechanisms involved in the expression of STP and LTP at CA1 synapses in the hippocampus.Neuropharmacology. 2007 Jan;52(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2006.06.017. Epub 2006 Aug 21. Neuropharmacology. 2007. PMID: 16919682 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuron-glia communication via EphA4/ephrin-A3 modulates LTP through glial glutamate transport.Nat Neurosci. 2009 Oct;12(10):1285-92. doi: 10.1038/nn.2394. Epub 2009 Sep 6. Nat Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19734893 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Visual Experience Leads to Potentiation of Spontaneous Activity in Mouse Superior Colliculus.Neurosci Bull. 2021 Mar;37(3):353-368. doi: 10.1007/s12264-020-00622-3. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Neurosci Bull. 2021. PMID: 33394455 Free PMC article.
-
Control of Long-Term Plasticity by Glutamate Transporters.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2019 Apr 9;11:10. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2019.00010. eCollection 2019. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31024287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutamate Transporters in Hippocampal LTD/LTP: Not Just Prevention of Excitotoxicity.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Aug 6;13:357. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00357. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31447647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction between the glutamate transporter GLT1b and the synaptic PDZ domain protein PICK1.Eur J Neurosci. 2008 Jan;27(1):66-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05986.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18184314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abel T, Nguyen PV, Barad M, Deuel TA, Kandel ER, Bourtchouladze R. Genetic demonstration of a role for PKA in the late phase of LTP and in hippocampus-based long-term memory. Cell. 1997;88:615–626. - PubMed
-
- Bliss TV, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993;361:31–39. - PubMed
-
- Cabell L, Audesirk G. Effects of selective inhibition of protein kinase C, cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, and Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase on neurite development in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1993;11:357–368. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

