Knockout of Slc25a19 causes mitochondrial thiamine pyrophosphate depletion, embryonic lethality, CNS malformations, and anemia
- PMID: 17035501
- PMCID: PMC1595310
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0607661103
Knockout of Slc25a19 causes mitochondrial thiamine pyrophosphate depletion, embryonic lethality, CNS malformations, and anemia
Abstract
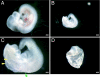
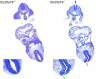
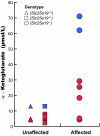
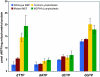
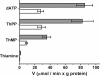
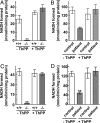
SLC25A19 mutations cause Amish lethal microcephaly (MCPHA), which markedly retards brain development and leads to alpha-ketoglutaric aciduria. Previous data suggested that SLC25A19, also called DNC, is a mitochondrial deoxyribonucleotide transporter. We generated a knockout mouse model of Slc25a19. These animals had 100% prenatal lethality by embryonic day 12. Affected embryos at embryonic day 10.5 have a neural-tube closure defect with ruffling of the neural fold ridges, a yolk sac erythropoietic failure, and elevated alpha-ketoglutarate in the amniotic fluid. We found that these animals have normal mitochondrial ribo- and deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate levels, suggesting that transport of these molecules is not the primary role of SLC25A19. We identified thiamine pyrophosphate (ThPP) transport as a candidate function of SLC25A19 through homology searching and confirmed it by using transport assays of the recombinant reconstituted protein. The mitochondria of Slc25a19(-/-) and MCPHA cells have undetectable and markedly reduced ThPP content, respectively. The reduction of ThPP levels causes dysfunction of the alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, which explains the high levels of this organic acid in MCPHA and suggests that mitochondrial ThPP transport is important for CNS development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
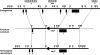
Similar articles
-
The evidence that the DNC (SLC25A19) is not the mitochondrial deoxyribonucleotide carrier.Mitochondrion. 2008 Mar;8(2):103-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2008.01.001. Epub 2008 Jan 18. Mitochondrion. 2008. PMID: 18280798 Review.
-
Adaptive regulation of pancreatic acinar mitochondrial thiamin pyrophosphate uptake process: possible involvement of epigenetic mechanism(s).Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017 Nov 1;313(5):G448-G455. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00192.2017. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28729247 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic alcohol exposure affects pancreatic acinar mitochondrial thiamin pyrophosphate uptake: studies with mouse 266-6 cell line and primary cells.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Nov 1;309(9):G750-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00226.2015. Epub 2015 Aug 27. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26316591 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of pancreatic acinar mitochondrial thiamin pyrophosphate uptake by the cigarette smoke component 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016 May 15;310(10):G874-83. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00461.2015. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26999808 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic defects of thiamine transport and metabolism: A review of clinical phenotypes, genetics, and functional studies.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2019 Jul;42(4):581-597. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12125. Epub 2019 Jun 24. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2019. PMID: 31095747 Review.
Cited by
-
SLC transporters as therapeutic targets: emerging opportunities.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015 Aug;14(8):543-60. doi: 10.1038/nrd4626. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015. PMID: 26111766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fetal and obstetrics manifestations of mitochondrial diseases.J Transl Med. 2024 Sep 23;22(1):853. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05633-6. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39313811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurological, Psychiatric, and Biochemical Aspects of Thiamine Deficiency in Children and Adults.Front Psychiatry. 2019 Apr 4;10:207. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00207. eCollection 2019. Front Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31019473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UCP2 transports C4 metabolites out of mitochondria, regulating glucose and glutamine oxidation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jan 21;111(3):960-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1317400111. Epub 2014 Jan 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24395786 Free PMC article.
-
Defects of thiamine transport and metabolism.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2014 Jul;37(4):577-85. doi: 10.1007/s10545-014-9712-9. Epub 2014 May 1. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2014. PMID: 24789339 Review.
References
-
- Kelley RI, Robinson D, Puffenberger EG, Strauss KA, Morton DH. Am J Med Genet. 2002;112:318–326. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg MJ, Agarwala R, Bouffard G, Davis J, Fiermonte G, Hilliard MS, Koch T, Kalikin LM, Makalowska I, Morton DH, et al. Nat Genet. 2002;32:175–179. - PubMed
-
- Palmieri F. Pflügers Arch. 2004;447:689–709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

