Dysfunctional KEAP1-NRF2 interaction in non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 17020408
- PMCID: PMC1584412
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030420
Dysfunctional KEAP1-NRF2 interaction in non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Nuclear factor erythroid-2 related factor 2 (NRF2) is a redox-sensitive transcription factor that positively regulates the expression of genes encoding antioxidants, xenobiotic detoxification enzymes, and drug efflux pumps, and confers cytoprotection against oxidative stress and xenobiotics in normal cells. Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) negatively regulates NRF2 activity by targeting it to proteasomal degradation. Increased expression of cellular antioxidants and xenobiotic detoxification enzymes has been implicated in resistance of tumor cells against chemotherapeutic drugs.
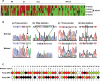
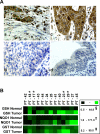
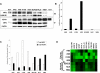
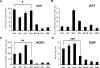
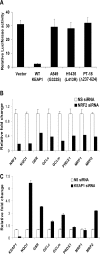
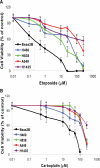
Methods and findings: Here we report a systematic analysis of the KEAP1 genomic locus in lung cancer patients and cell lines that revealed deletion, insertion, and missense mutations in functionally important domains of KEAP1 and a very high percentage of loss of heterozygosity at 19p13.2, suggesting that biallelic inactivation of KEAP1 in lung cancer is a common event. Sequencing of KEAP1 in 12 cell lines and 54 non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) samples revealed somatic mutations in KEAP1 in a total of six cell lines and ten tumors at a frequency of 50% and 19%, respectively. All the mutations were within highly conserved amino acid residues located in the Kelch or intervening region domain of the KEAP1 protein, suggesting that these mutations would likely abolish KEAP1 repressor activity. Evaluation of loss of heterozygosity at 19p13.2 revealed allelic losses in 61% of the NSCLC cell lines and 41% of the tumor samples. Decreased KEAP1 activity in cancer cells induced greater nuclear accumulation of NRF2, causing enhanced transcriptional induction of antioxidants, xenobiotic metabolism enzymes, and drug efflux pumps.
Conclusions: This is the first study to our knowledge to demonstrate that biallelic inactivation of KEAP1 is a frequent genetic alteration in NSCLC. Loss of KEAP1 function leading to constitutive activation of NRF2-mediated gene expression in cancer suggests that tumor cells manipulate the NRF2 pathway for their survival against chemotherapeutic agents.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular mechanisms for the regulation of Nrf2-mediated cell proliferation in non-small-cell lung cancers.Oncogene. 2012 Nov 8;31(45):4768-77. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.628. Epub 2012 Jan 16. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 22249257
-
RNAi-mediated silencing of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 gene expression in non-small cell lung cancer inhibits tumor growth and increases efficacy of chemotherapy.Cancer Res. 2008 Oct 1;68(19):7975-84. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1401. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18829555 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory role of KEAP1 and NRF2 in PPARγ expression and chemoresistance in human non-small-cell lung carcinoma cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2012 Aug 15;53(4):758-68. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.05.041. Epub 2012 Jun 7. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 22684020 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of Nrf2 signal in non-small cell lung cancer.J Hematol Oncol. 2016 Feb 27;9:14. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0246-5. J Hematol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26922479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of the Keap1–Nrf2 pathway in stress response and cancer evolution.Genes Cells. 2011 Feb;16(2):123-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2010.01473.x. Genes Cells. 2011. PMID: 21251164 Review.
Cited by
-
Cross-regulations among NRFs and KEAP1 and effects of their silencing on arsenic-induced antioxidant response and cytotoxicity in human keratinocytes.Environ Health Perspect. 2012 Apr;120(4):583-9. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1104580. Epub 2012 Jan 3. Environ Health Perspect. 2012. PMID: 22476201 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of antioxidants which play the role in cellular response against oxidative/nitrosative stress: current state.Nutr J. 2016 Jul 25;15(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12937-016-0186-5. Nutr J. 2016. PMID: 27456681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small Molecule Inhibitor of NRF2 Selectively Intervenes Therapeutic Resistance in KEAP1-Deficient NSCLC Tumors.ACS Chem Biol. 2016 Nov 18;11(11):3214-3225. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.6b00651. Epub 2016 Oct 17. ACS Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 27552339 Free PMC article.
-
p62-Induced Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Activation via the Nrf2-ATF6 Pathway Promotes Lung Tumorigenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 18;13(4):864. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040864. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33670717 Free PMC article.
-
Aldo-keto reductases are biomarkers of NRF2 activity and are co-ordinately overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer.Br J Cancer. 2016 Dec 6;115(12):1530-1539. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2016.363. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Br J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27824809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spiro SG, Silvestri GA. The treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2005;11:287–291. - PubMed
-
- Tsai CM, Chang KT, Perng RP, Mitsudomi T, Chen MH, et al. Correlation of intrinsic chemoresistance of non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines with HER-2/neu gene expression but not with ras gene mutations. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993;85:897–901. - PubMed
-
- Tew KD. Glutathione-associated enzymes in anticancer drug resistance. Cancer Res. 1994;54:4313–4320. - PubMed
-
- Young LC, Campling BG, Cole SP, Deeley RG, Gerlach JH. Multidrug resistance proteins MRP3, MRP1, and MRP2 in lung cancer: Correlation of protein levels with drug response and messenger RNA levels. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:1798–1804. - PubMed
-
- Soini Y, Napankangas U, Jarvinen K, Kaarteenaho-Wiik R, Paakko P, et al. Expression of gamma-glutamyl cysteine synthetase in nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer. 2001;92:2911–2919. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

