Suppression of Mcl-1 via RNA interference sensitizes human hepatocellular carcinoma cells towards apoptosis induction
- PMID: 17014711
- PMCID: PMC1601962
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-232
Suppression of Mcl-1 via RNA interference sensitizes human hepatocellular carcinoma cells towards apoptosis induction
Abstract
Background: Hepatocelluar carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cancers worldwide and a major cause of cancer-related mortality. HCC is highly resistant to currently available chemotherapeutic drugs. Defects in apoptosis signaling contribute to this resistance. Myeloid cell leukemia-1 (Mcl-1) is an anti-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 protein family which interferes with mitochondrial activation. In a previous study we have shown that Mcl-1 is highly expressed in tissues of human HCC. In this study, we manipulated expression of the Mcl-1 protein in HCC cells by RNA interference and analyzed its impact on apoptosis sensitivity of HCC cells in vitro.
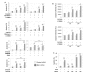
Methods: RNA interference was performed by transfecting siRNA to specifically knock down Mcl-1 expression in HCC cells. Mcl-1 expression was measured by quantitative real-time PCR and Western blot. Induction of apoptosis and caspase activity after treatment with chemotherapeutic drugs and different targeted therapies were measured by flow cytometry and fluorometric analysis, respectively.
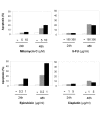
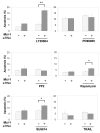
Results: Here we demonstrate that Mcl-1 expressing HCC cell lines show low sensitivity towards treatment with a panel of chemotherapeutic drugs. However, treatment with the anthracycline derivative epirubicin resulted in comparatively high apoptosis rates in HCC cells. Inhibition of the kinase PI3K significantly increased apoptosis induction by chemotherapy. RNA interference efficiently downregulated Mcl-1 expression in HCC cells. Mcl-1 downregulation sensitized HCC cells to different chemotherapeutic agents. Sensitization was accompanied by profound activation of caspase-3 and -9. In addition, Mcl-1 downregulation also increased apoptosis rates after treatment with PI3K inhibitors and, to a lower extent, after treatment with mTOR, Raf I and VEGF/PDGF kinase inhibitors. TRAIL-induced apoptosis did not markedly respond to Mcl-1 knockdown. Additionally, knockdown of Mcl-1 efficiently enhanced apoptosis sensitivity towards combined treatment modalities: Mcl-1 knockdown significantly augmented apoptosis sensitivity of HCC cells towards chemotherapy combined with PI3K inhibition.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that specific downregulation of Mcl-1 by RNA interference is a promising approach to sensitize HCC cells towards chemotherapy and molecularly targeted therapies.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mcl-1 is an anti-apoptotic factor for human hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Oncol. 2006 Jan;28(1):25-32. Int J Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16327976
-
Mcl-1 overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma: a potential target for antisense therapy.J Hepatol. 2006 Jan;44(1):151-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2005.09.010. Epub 2005 Oct 25. J Hepatol. 2006. PMID: 16289418
-
Bid sensitizes apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic drugs in hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Oncol. 2004 Sep;25(3):651-9. Int J Oncol. 2004. PMID: 15289866
-
Targeted therapy of hepatocellular cancer.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010 Feb;19(2):265-74. doi: 10.1517/13543780903514110. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20074016 Review.
-
Expression of IAPs and alternative splice variants in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues and cells.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004 Dec;1028:289-93. doi: 10.1196/annals.1322.033. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004. PMID: 15650254 Review.
Cited by
-
Baicalein, a component of Scutellaria baicalensis, induces apoptosis by Mcl-1 down-regulation in human pancreatic cancer cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Aug;1813(8):1465-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.05.003. Epub 2011 May 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21596068 Free PMC article.
-
Ablation of MCL1 expression by virally induced microRNA-29 reverses chemoresistance in human osteosarcomas.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 30;6:28953. doi: 10.1038/srep28953. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27356624 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of HBx by RNAi inhibits proliferation and enhances chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Med Oncol. 2010 Dec;27(4):1227-33. doi: 10.1007/s12032-009-9363-0. Epub 2009 Dec 1. Med Oncol. 2010. PMID: 19949899
-
Knockout of myeloid cell leukemia-1 induces liver damage and increases apoptosis susceptibility of murine hepatocytes.Hepatology. 2009 Feb;49(2):627-36. doi: 10.1002/hep.22664. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19127517 Free PMC article.
-
Role of MicroRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Hepat Mon. 2014 Aug 1;14(8):e18672. doi: 10.5812/hepatmon.18672. eCollection 2014 Aug. Hepat Mon. 2014. PMID: 25337143 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

