An enteroendocrine cell-based model for a quiescent intestinal stem cell niche
- PMID: 16987141
- PMCID: PMC6496364
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2006.00396.x
An enteroendocrine cell-based model for a quiescent intestinal stem cell niche
Abstract
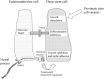
We have shown that the kinetics of conversion of intestinal crypt cell populations to a partially or wholly mutant phenotype are consistent with a model in which each crypt contains an infrequently dividing 'deep' stem cell that is the progenitor of several more frequently dividing 'proximate' stem cells. An assumption of our model is that each deep stem cell exists in a growth inhibitory niche. We have used information from the literature to develop a model for a quiescent intestinal stem cell niche. This niche is postulated to be primarily defined by an enteroendocrine cell type that maintains stem cell quiescence by secretion of growth inhibitory peptides such as somatostatin and guanylin/uroguanylin. Consistent with this model, there is evidence that the proteins postulated as defining a growth-inhibitory stem cell niche can act as intestinal tumour suppressors. Confirmation that a growth-inhibitory niche does exist would have important implications for our understanding of intestinal homeostasis and tumorigenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intestinal crypt properties fit a model that incorporates replicative ageing and deep and proximate stem cells.Cell Prolif. 2006 Oct;39(5):379-402. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2006.00395.x. Cell Prolif. 2006. PMID: 16987140 Free PMC article.
-
Enteroendocrine cells support intestinal stem-cell-mediated homeostasis in Drosophila.Cell Rep. 2014 Oct 9;9(1):32-39. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.08.052. Epub 2014 Sep 25. Cell Rep. 2014. PMID: 25263551 Free PMC article.
-
Neurogenin 3 and the enteroendocrine cell lineage in the adult mouse small intestinal epithelium.Dev Biol. 2006 Dec 15;300(2):722-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.07.040. Epub 2006 Aug 7. Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 17007831
-
Basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors and enteroendocrine cell differentiation.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011 Oct;13 Suppl 1(0 1):5-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2011.01438.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011. PMID: 21824251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enteroendocrine cell types revisited.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013 Dec;13(6):912-21. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2013.09.018. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24140256 Review.
Cited by
-
Intestinal crypt properties fit a model that incorporates replicative ageing and deep and proximate stem cells.Cell Prolif. 2006 Oct;39(5):379-402. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2006.00395.x. Cell Prolif. 2006. PMID: 16987140 Free PMC article.
-
Aging of the mammalian gastrointestinal tract: a complex organ system.Age (Dordr). 2014 Jun;36(3):9603. doi: 10.1007/s11357-013-9603-2. Epub 2013 Dec 20. Age (Dordr). 2014. PMID: 24352567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive model of the spatio-temporal stem cell and tissue organisation in the intestinal crypt.PLoS Comput Biol. 2011 Jan 6;7(1):e1001045. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1001045. PLoS Comput Biol. 2011. PMID: 21253562 Free PMC article.
-
Label-retaining assay enriches tumor-initiating cells in glioblastoma spheres cultivated in serum-free medium.Oncol Lett. 2016 Aug;12(2):815-824. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4690. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27446356 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory niche of intestinal stem cells.J Physiol. 2016 Sep 1;594(17):4827-36. doi: 10.1113/JP271931. Epub 2016 Jul 28. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27060879 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alderton F, Humphrey PPA, Sellers LA (2001) High‐intensity p38 kinase activity is critical for p21cip1 induction and the antiproliferative function of Gi protein‐coupled receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 59, 1119–1128. - PubMed
-
- Anant S, Murmu N, Houchen CW, Mukhopadhyay D, Riehl TE, Young SG, Morrison AR, Stenson WF, Davidson NO (2004) Apobec‐1 protects intestine from radiation injury through posttranscriptional regulation of cyclooxygenase‐2 expression. Gastroenterology 127, 1139–1149. - PubMed
-
- Arai F, Hirao A, Ohmura M, Sato H, Matsuoka S, Takubo K, Ito K, Koh GY, Suda T (2004) Tie2/Angiopoietin‐1 signaling regulates hematopoietic stem cell quiescence in the bone marrow niche. Cell 118, 149–161. - PubMed
-
- Arebi N, Healey ZV, Bliss PW, Ghatei M, Van Noorden S, Playford RJ, Calam J (2002) Nitric oxide regulates the release of somatostatin from cultured gastric rabbit primary D‐cells. Gastroenterology 123, 566–576. - PubMed
-
- Bardelli A, Parsons DW, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, Saha S, Markowitz. S, Willson JK, Parmigiani G, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Velculescu VE (2003) Mutational analysis of the tyrosine kinome in colorectal cancers. Science 300, 949. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical