Full and partial genome-wide assembly and disassembly of the yeast transcription machinery in response to heat shock
- PMID: 16912275
- PMCID: PMC1553208
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1437506
Full and partial genome-wide assembly and disassembly of the yeast transcription machinery in response to heat shock
Abstract
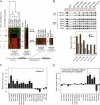
Eukaryotic genes are controlled by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins, chromatin regulators, general transcription factors, and elongation factors. Here we examine the genome-wide location of representative members of these groups and their redistribution when the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome is reprogrammed by heat shock. As expected, assembly of active transcription complexes is coupled to eviction of H2A.Z nucleosomes, and disassembly is coupled to the return of nucleosomes. Remarkably, a large number of promoters assemble into partial preinitiation complexes (partial PICs), containing TFIIA, TFIID (and/or SAGA), TFIIB, TFIIE, and TFIIF. However, RNA polymerase II and TFIIH are generally not recruited, and nucleosomes are not displaced. These promoters may be preparing for additional stress that naturally accompany heat stress. For example, we find that oxidative stress, which often occurs with prolonged exposure of cells to high temperature, converts partial PICs into full PICs. Partial PICs therefore represent novel regulated intermediates that assemble at promoters in the midst of chromatin.
Figures
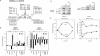

Similar articles
-
Domain-wide displacement of histones by activated heat shock factor occurs independently of Swi/Snf and is not correlated with RNA polymerase II density.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Oct;25(20):8985-99. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.20.8985-8999.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16199876 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide structure and organization of eukaryotic pre-initiation complexes.Nature. 2012 Jan 18;483(7389):295-301. doi: 10.1038/nature10799. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22258509 Free PMC article.
-
Different requirements of the SWI/SNF complex for robust nucleosome displacement at promoters of heat shock factor and Msn2- and Msn4-regulated heat shock genes.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Feb;28(4):1207-17. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01069-07. Epub 2007 Dec 10. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18070923 Free PMC article.
-
The role of chromatin structure in regulating stress-induced transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochem Cell Biol. 2006 Aug;84(4):477-89. doi: 10.1139/o06-079. Biochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16936821 Review.
-
Primary Role of the Nucleosome.Mol Cell. 2020 Aug 6;79(3):371-375. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.07.020. Mol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32763226 Review.
Cited by
-
The transcriptional repressor activator protein Rap1p is a direct regulator of TATA-binding protein.J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 28;283(13):8699-710. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M709436200. Epub 2008 Jan 14. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18195009 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleosome positioning and gene regulation: advances through genomics.Nat Rev Genet. 2009 Mar;10(3):161-72. doi: 10.1038/nrg2522. Nat Rev Genet. 2009. PMID: 19204718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NuA4-directed chromatin transactions throughout the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Aug;27(15):5327-35. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00468-07. Epub 2007 May 25. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17526728 Free PMC article.
-
Adr1 and Cat8 mediate coactivator recruitment and chromatin remodeling at glucose-regulated genes.PLoS One. 2008 Jan 16;3(1):e1436. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001436. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18197247 Free PMC article.
-
Identification, structure, and functional requirement of the Mediator submodule Med7N/31.EMBO J. 2009 Jan 7;28(1):69-80. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.254. Epub 2008 Dec 4. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19057509 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akoulitchev S., Makela T.P., Weinberg R.A., Reinberg D. Requirement for TFIIH kinase activity in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1995;377:557–560. - PubMed
-
- Basehoar A.D., Zanton S.J., Pugh B.F. Identification and distinct regulation of yeast TATA box-containing genes. Cell. 2004;116:699–709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
