Expression and function of SNAP-25 as a universal SNARE component in GABAergic neurons
- PMID: 16870728
- PMCID: PMC6674219
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1866-06.2006
Expression and function of SNAP-25 as a universal SNARE component in GABAergic neurons
Erratum in
- J Neurosci. 2006 Aug 23;26(34):8875
Abstract
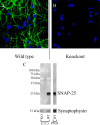
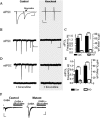
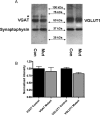
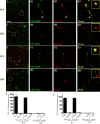
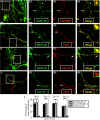
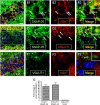
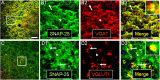
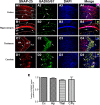
Intracellular vesicular trafficking and membrane fusion are important processes for nervous system development and for the function of neural circuits. Synaptosomal-associated protein 25 kDa (SNAP-25) is a component of neural soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) core complexes that mediate the exocytotic release of neurotransmitters at chemical synapses. Previous results from mouse mutant models and pharmacological/neurotoxin blockades have demonstrated a critical role for SNAP-25-containing SNARE complexes in action potential (AP)-dependent release at cholinergic and glutamatergic synapses and for calcium-triggered catecholamine release from chromaffin cells. To examine whether SNAP-25 participates in the evoked release of other neurotransmitters, we investigated the expression and function of SNAP-25 in GABAergic terminals. Patch-clamp recordings in fetal Snap25-null mutant cortex demonstrated that ablation of SNAP-25 eliminated evoked GABA(A) receptor-mediated postsynaptic responses while leaving a low level of spontaneous AP-independent events intact, supporting the involvement of SNAP-25 in the regulated synaptic transmission of early developing GABAergic neurons. In hippocampal cell cultures of wild-type mice, punctate staining of SNAP-25 colocalized with both GABAergic and glutamatergic synaptic markers, whereas stimulus-evoked vesicular recycling was abolished at terminals of both transmitter phenotypes in Snap25-/- neurons. Moreover, immunohistochemistry and fluorescence in situ hybridization revealed coexpression of SNAP-25, VGAT (vesicular GABA transporter), and GAD65/67 (glutamic acid decarboxylase 65/67) in interneurons within several regions of the adult brain. Our results thus provide evidence that SNAP-25 is critical for evoked GABA release during development and is expressed in the presynaptic terminals of mature GABAergic neurons, consistent with its function as a component of a fundamental core SNARE complex required for stimulus-driven neurotransmission.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of the t-SNARE SNAP-25 in action potential-dependent calcium signaling and expression in GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons.BMC Neurosci. 2008 Oct 29;9:105. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-9-105. BMC Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18959796 Free PMC article.
-
SNAP-25 modulation of calcium dynamics underlies differences in GABAergic and glutamatergic responsiveness to depolarization.Neuron. 2004 Feb 19;41(4):599-610. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(04)00077-7. Neuron. 2004. PMID: 14980208
-
Analysis of SNAP-25 immunoreactivity in hippocampal inhibitory neurons during development in culture and in situ.Neuroscience. 2005;131(4):813-23. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.11.042. Neuroscience. 2005. PMID: 15749336
-
The synaptic split of SNAP-25: different roles in glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons?Neuroscience. 2009 Jan 12;158(1):223-30. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.03.014. Epub 2008 Mar 20. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 18514426 Review. No abstract available.
-
The SNAP-25 Protein Family.Neuroscience. 2019 Nov 10;420:50-71. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.09.020. Epub 2018 Sep 27. Neuroscience. 2019. PMID: 30267828 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of the t-SNARE SNAP-25 in action potential-dependent calcium signaling and expression in GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons.BMC Neurosci. 2008 Oct 29;9:105. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-9-105. BMC Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18959796 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive and evoked release of ATP in adult mouse olfactory epithelium.Open Life Sci. 2024 Jan 16;19(1):20220811. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0811. eCollection 2024. Open Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38250473 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of miR-1 in the heart attenuates hippocampal synaptic vesicle exocytosis by the posttranscriptional regulation of SNAP-25 through the transportation of exosomes.Cell Commun Signal. 2018 Nov 29;16(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s12964-018-0303-5. Cell Commun Signal. 2018. PMID: 30497498 Free PMC article.
-
SNAP25 expression in mammalian retinal horizontal cells.J Comp Neurol. 2011 Apr 1;519(5):972-88. doi: 10.1002/cne.22562. J Comp Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21280047 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism underlying unaltered cortical inhibitory synaptic transmission in contrast with enhanced excitatory transmission in CaV2.1 knockin migraine mice.Neurobiol Dis. 2014 Sep;69(100):225-34. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.05.035. Epub 2014 Jun 5. Neurobiol Dis. 2014. PMID: 24907493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Augustin I, Rosenmund C, Sudhof TC, Brose N (1999). Munc13-1 is essential for fusion competence of glutamatergic synaptic vesicles. Nature 400:457–461. - PubMed
-
- Bedet C, Isambert MF, Henry JP, Gasnier B (2000). Constitutive phosphorylation of the vesicular inhibitory amino acid transporter in rat central nervous system. J Neurochem 75:1654–1663. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
