Inhibition of ribosome recruitment induces stress granule formation independently of eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha phosphorylation
- PMID: 16870703
- PMCID: PMC1635342
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e06-04-0318
Inhibition of ribosome recruitment induces stress granule formation independently of eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha phosphorylation
Abstract
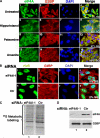
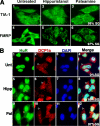
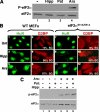
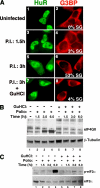
Cytoplasmic aggregates known as stress granules (SGs) arise as a consequence of cellular stress and contain stalled translation preinitiation complexes. These foci are thought to serve as sites of mRNA storage or triage during the cell stress response. SG formation has been shown to require induction of eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF)2alpha phosphorylation. Herein, we investigate the potential role of other initiation factors in this process and demonstrate that interfering with eIF4A activity, an RNA helicase required for the ribosome recruitment phase of translation initiation, induces SG formation and that this event is not dependent on eIF2alpha phosphorylation. We also show that inhibition of eIF4A activity does not impair the ability of eIF2alpha to be phosphorylated under stress conditions. Furthermore, we observed SG assembly upon inhibition of cap-dependent translation after poliovirus infection. We propose that SG modeling can occur via both eIF2alpha phosphorylation-dependent and -independent pathways that target translation initiation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Uncoupling stress granule assembly and translation initiation inhibition.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Jun;20(11):2673-83. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-10-1061. Epub 2009 Apr 15. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19369421 Free PMC article.
-
G3BP-Caprin1-USP10 complexes mediate stress granule condensation and associate with 40S subunits.J Cell Biol. 2016 Mar 28;212(7):845-60. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201508028. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27022092 Free PMC article.
-
Newcastle disease virus induces stable formation of bona fide stress granules to facilitate viral replication through manipulating host protein translation.FASEB J. 2017 Apr;31(4):1337-1353. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600980R. Epub 2016 Dec 23. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28011649
-
eIF4 initiation factors: effectors of mRNA recruitment to ribosomes and regulators of translation.Annu Rev Biochem. 1999;68:913-63. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.68.1.913. Annu Rev Biochem. 1999. PMID: 10872469 Review.
-
Stress Granules and Acute Ischemic Stroke: Beyond mRNA Translation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 29;23(7):3747. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073747. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409112 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stress granules dynamics: benefits in cancer.BMB Rep. 2022 Dec;55(12):577-586. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2022.55.12.141. BMB Rep. 2022. PMID: 36330685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inactivation of the mTORC1-eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E pathway alters stress granule formation.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jun;33(11):2285-301. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01517-12. Epub 2013 Apr 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23547259 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of stress granules and P-bodies during RNA virus infection.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2013 May-Jun;4(3):317-31. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1162. Epub 2013 Apr 3. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2013. PMID: 23554219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Herpes simplex virus 2 infection impacts stress granule accumulation.J Virol. 2012 Aug;86(15):8119-30. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00313-12. Epub 2012 May 23. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22623775 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative genomics positions MKRN1 as a novel ribonucleoprotein within the embryonic stem cell gene regulatory network.EMBO Rep. 2015 Oct;16(10):1334-57. doi: 10.15252/embr.201540974. Epub 2015 Aug 11. EMBO Rep. 2015. PMID: 26265008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bordeleau M.-E., Matthews J., Wojnar J. M., Lindqvist L., Novac O., Jankowsky E., Sonenberg N., Northcote P., Teesdale-Spittle P., Pelletier J. Stimulation of mammalian translation initiation factor eIF4A. activity by a small molecule inhibitor of eukaryotic translation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:10460–10465. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

