Factors regulating the abundance and localization of synaptobrevin in the plasma membrane
- PMID: 16844789
- PMCID: PMC1544097
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0600784103
Factors regulating the abundance and localization of synaptobrevin in the plasma membrane
Abstract
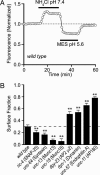
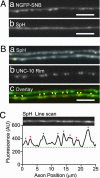
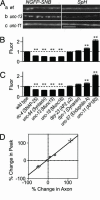
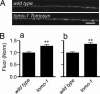
After synaptic vesicle fusion, vesicle proteins must be segregated from plasma membrane proteins and recycled to maintain a functional vesicle pool. We monitored the distribution of synaptobrevin, a vesicle protein required for exocytosis, in Caenorhabditis elegans motor neurons by using a pH-sensitive synaptobrevin GFP fusion protein, synaptopHluorin. We estimated that 30% of synaptobrevin was present in the plasma membrane. By using a panel of endocytosis and exocytosis mutants, we found that the majority of surface synaptobrevin derives from fusion of synaptic vesicles and that, in steady state, synaptobrevin equilibrates throughout the axon. The surface synaptobrevin was enriched near active zones, and its spatial extent was regulated by the clathrin adaptin AP180. These results suggest that there is a plasma membrane reservoir of synaptobrevin that is supplied by the synaptic vesicle cycle and available for retrieval throughout the axon. The size of the reservoir is set by the relative rates of exo- and endocytosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AP180 maintains the distribution of synaptic and vesicle proteins in the nerve terminal and indirectly regulates the efficacy of Ca2+-triggered exocytosis.J Neurophysiol. 2005 Sep;94(3):1888-903. doi: 10.1152/jn.00080.2005. Epub 2005 May 11. J Neurophysiol. 2005. PMID: 15888532
-
SNARE motif-mediated sorting of synaptobrevin by the endocytic adaptors clathrin assembly lymphoid myeloid leukemia (CALM) and AP180 at synapses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Aug 16;108(33):13540-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1107067108. Epub 2011 Aug 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21808019 Free PMC article.
-
UNC-11, a Caenorhabditis elegans AP180 homologue, regulates the size and protein composition of synaptic vesicles.Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Jul;10(7):2343-60. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.7.2343. Mol Biol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10397769 Free PMC article.
-
Turning CALM into excitement: AP180 and CALM in endocytosis and disease.Biol Cell. 2012 Oct;104(10):588-602. doi: 10.1111/boc.201200008. Epub 2012 May 31. Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22639918 Review.
-
The Sybtraps: control of synaptobrevin traffic by synaptophysin, α-synuclein and AP-180.Traffic. 2014 Mar;15(3):245-54. doi: 10.1111/tra.12140. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Traffic. 2014. PMID: 24279465 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Male pheromones modulate synaptic transmission at the C. elegans neuromuscular junction in a sexually dimorphic manner.Elife. 2021 Mar 31;10:e67170. doi: 10.7554/eLife.67170. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33787493 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of synaptophysin: a hexameric MARVEL-domain channel protein.Structure. 2007 Jun;15(6):707-14. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2007.04.011. Structure. 2007. PMID: 17562317 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptophysin I selectively specifies the exocytic pathway of synaptobrevin 2/VAMP2.Biochem J. 2007 Jun 15;404(3):525-34. doi: 10.1042/BJ20061907. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17331077 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic autophagy is coupled to the synaptic vesicle cycle via ATG-9.Neuron. 2022 Mar 2;110(5):824-840.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.12.031. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Neuron. 2022. PMID: 35065714 Free PMC article.
-
Endocytic adaptors--social networking at the plasma membrane.J Cell Sci. 2011 May 15;124(Pt 10):1613-22. doi: 10.1242/jcs.073395. J Cell Sci. 2011. PMID: 21536832 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Betz W. J., Angleson J. K. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1998;60:347–363. - PubMed
-
- Schneggenburger R., Sakaba T., Neher E. Trends Neurosci. 2002;25:206–212. - PubMed
-
- von Gersdorff H., Matthews G. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1999;61:725–752. - PubMed
-
- Calakos N., Scheller R. H. Physiol. Rev. 1996;76:1–29. - PubMed
-
- Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1999;68:863–911. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

