Plasminogen-mediated activation and release of hepatocyte growth factor from extracellular matrix
- PMID: 16840775
- PMCID: PMC2643296
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2006-0006OC
Plasminogen-mediated activation and release of hepatocyte growth factor from extracellular matrix
Abstract
Interventions that enhance plasminogen activation within the lung consistently limit the fibrosis that follows alveolar injury. However, this protective effect cannot be attributed solely to accelerated clearance of fibrin that forms as a provisional matrix after lung injury. To explore other mechanisms, we considered interactions between the plasminogen activation system and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). HGF is known to have antifibrotic activity, but to do so, it must be both released from its sites of sequestration within extracellular matrix (ECM) and activated by proteolytic cleavage. A recent study using bleomycin-exposed mice showed that manipulations of the plasminogen activation system influenced the amount of free HGF within bronchoalveolar lavage fluid without affecting total lung HGF mRNA or protein. To elucidate the mechanisms, we studied the role of plasminogen activation in fibroblast-mediated HGF release and activation. We found that NIH3T3 and mouse lung fibroblasts release ECM-bound HGF in a plasminogen-dependent fashion. The plasminogen effect was lost when lung fibroblasts from urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA)-deficient mice were used, and was increased by fibroblasts from plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI)-1-deficient mice. Plasminogen addition to NIH3T3 or mouse lung fibroblasts increased conversion of pro-HGF to its active form. The plasminogen effect on activation was lost when uPA-deficient fibroblasts were used and accentuated by PAI-1-deficient fibroblasts. In conjunction with the previous in vivo study, these results suggest that plasminogen activation can protect the lung against fibrosis by increasing the availability of active HGF.
Figures



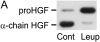
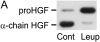
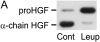


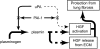
Similar articles
-
The antifibrotic effects of plasminogen activation occur via prostaglandin E2 synthesis in humans and mice.J Clin Invest. 2010 Jun;120(6):1950-60. doi: 10.1172/JCI38369. Epub 2010 May 24. J Clin Invest. 2010. PMID: 20501949 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous urokinase lacks antifibrotic activity during progressive renal injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007 Jul;293(1):F12-9. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00380.2006. Epub 2007 Mar 13. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17356128
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 suppresses profibrotic responses in fibroblasts from fibrotic lungs.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 10;290(15):9428-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.601815. Epub 2015 Feb 3. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25648892 Free PMC article.
-
The fibrogenic actions of the coagulant and plasminogen activation systems in pulmonary fibrosis.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018 Apr;97:108-117. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2018.02.016. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29474926 Review.
-
Hepatocyte growth factor in lung repair and pulmonary fibrosis.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011 Jan;32(1):12-20. doi: 10.1038/aps.2010.90. Epub 2010 Dec 6. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011. PMID: 21131996 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Distinguishing Plasmin-Generating Microvesicles: Tiny Messengers Involved in Fibrinolysis and Proteolysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 13;24(2):1571. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021571. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosome-Mediated Activation of the Prostasin-Matriptase Serine Protease Cascade in B Lymphoma Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jul 28;15(15):3848. doi: 10.3390/cancers15153848. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568664 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of proteinases during mouse peri-implantation development: urokinase-type plasminogen activator expression and cross talk with matrix metalloproteinase 9.Reproduction. 2011 Feb;141(2):227-39. doi: 10.1530/REP-10-0334. Epub 2010 Nov 12. Reproduction. 2011. PMID: 21075828 Free PMC article.
-
Plasticity versus specificity in RTK signalling modalities for distinct biological outcomes in motor neurons.BMC Biol. 2014 Aug 14;12:56. doi: 10.1186/s12915-014-0056-6. BMC Biol. 2014. PMID: 25124859 Free PMC article.
-
Cell surface remodeling by plasmin: a new function for an old enzyme.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:564259. doi: 10.1155/2012/564259. Epub 2012 Oct 14. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 23097597 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Selman M, King TE, Pardo A. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: prevailing and evolving hypotheses about its pathogenesis and implications for therapy. Ann Intern Med 2001;134:136–151. - PubMed
-
- Sisson TH, Simon RH. Cell specific control of coagulation and fibrinolysis within the lung. Thromb Haemost 2004;92:435–437. - PubMed
-
- Chapman HA, Allen CL, Stone OL. Abnormalities in pathways of alveolar fibrin turnover among patients with interstitial lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis 1986;133:437–443. - PubMed
-
- Bertozzi P, Astedt B, Zenzius L, Lynch K, LeMaire F, Zapol W, Chapman HA Jr. Depressed bronchoalveolar urokinase activity in patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 1990;322:890–897. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

