Selective small-molecule inhibitor reveals critical mitotic functions of human CDK1
- PMID: 16818887
- PMCID: PMC1502288
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0600447103
Selective small-molecule inhibitor reveals critical mitotic functions of human CDK1
Abstract
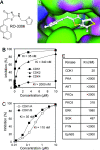
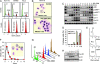
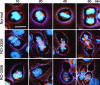
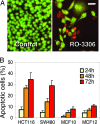
CDK1 is a nonredundant cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) with an essential role in mitosis, but its multiple functions still are poorly understood at a molecular level. Here we identify a selective small-molecule inhibitor of CDK1 that reversibly arrests human cells at the G(2)/M border of the cell cycle and allows for effective cell synchronization in early mitosis. Inhibition of CDK1 during cell division revealed that its activity is necessary and sufficient for maintaining the mitotic state of the cells, preventing replication origin licensing and premature cytokinesis. Although CDK1 inhibition for up to 24 h is well tolerated, longer exposure to the inhibitor induces apoptosis in tumor cells, suggesting that selective CDK1 inhibitors may have utility in cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Restoration of the tumor suppressor p53 by downregulating cyclin B1 in human papillomavirus 16/18-infected cancer cells.Oncogene. 2010 Oct 14;29(41):5591-603. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.290. Epub 2010 Jul 26. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 20661218
-
Cell cycle synchronization at the G2/M phase border by reversible inhibition of CDK1.Cell Cycle. 2006 Nov;5(22):2555-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.22.3463. Epub 2006 Nov 15. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 17172841
-
The cell cycle checkpoint kinase Chk2 is a negative regulator of mitotic catastrophe.Oncogene. 2004 May 27;23(25):4353-61. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207573. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15048074
-
The lethal response to Cdk1 inhibition depends on sister chromatid alignment errors generated by KIF4 and isoform 1 of PRC1.Sci Rep. 2015 Oct 1;5:14798. doi: 10.1038/srep14798. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26423135 Free PMC article.
-
Cdk1 and Cdk2 complexes (cyclin dependent kinases) in apoptosis: a role beyond the cell cycle.Cancer Lett. 2005 Jan 20;217(2):129-38. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2004.08.005. Cancer Lett. 2005. PMID: 15617830 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphorylation of islet-1 serine 269 by CDK1 increases its transcriptional activity and promotes cell proliferation in gastric cancer.Mol Med. 2021 May 7;27(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00302-6. Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33962568 Free PMC article.
-
PLK1-dependent activation of LRRK1 regulates spindle orientation by phosphorylating CDK5RAP2.Nat Cell Biol. 2015 Aug;17(8):1024-35. doi: 10.1038/ncb3204. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Nat Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26192437
-
NuMA interaction with chromatin is vital for proper chromosome decondensation at the mitotic exit.Mol Biol Cell. 2020 Oct 15;31(22):2437-2451. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-06-0415. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Mol Biol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32845810 Free PMC article.
-
Global Phosphoproteomic Mapping of Early Mitotic Exit in Human Cells Identifies Novel Substrate Dephosphorylation Motifs.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015 Aug;14(8):2194-212. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M114.046938. Epub 2015 Jun 8. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 26055452 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of phosphorylation of the mitotic centromere-associated kinesin by Aurora B kinase in human tumor cells.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(23):3755-67. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1068481. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 26148251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Norbury C., Nurse P. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1992;61:441–470. - PubMed
-
- Morgan D. O. Nature. 1995;374:131–134. - PubMed
-
- Murray A. W. Chem. Biol. 1994;1:191–195. - PubMed
-
- Tetsu O., McCormick F. Cancer Cell. 2003;3:233–245. - PubMed
-
- Ortega S., Prieto I., Odajima J., Martin A., Dubus P., Sotillo R., Barbero J. L., Malumbres M., Barbacid M. Nat. Genet. 2003;35:25–31. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

