Ubiquitin-like protein 5 positively regulates chaperone gene expression in the mitochondrial unfolded protein response
- PMID: 16816413
- PMCID: PMC1569816
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.061580
Ubiquitin-like protein 5 positively regulates chaperone gene expression in the mitochondrial unfolded protein response
Abstract
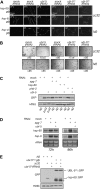
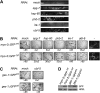
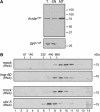
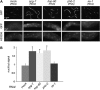
Perturbation of the protein-folding environment in the mitochondrial matrix selectively upregulates the expression of nuclear genes encoding mitochondrial chaperones. To identify components of the signal transduction pathway(s) mediating this mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPR(mt)), we first isolated a temperature-sensitive mutation (zc32) that conditionally activates the UPR(mt) in C. elegans and subsequently searched for suppressors by systematic inactivation of genes. RNAi of ubl-5, a gene encoding a ubiquitin-like protein, suppresses activation of the UPR(mt) markers hsp-60::gfp and hsp-6::gfp by the zc32 mutation and by other manipulations that promote mitochondrial protein misfolding. ubl-5 (RNAi) inhibits the induction of endogenous mitochondrial chaperone encoding genes hsp-60 and hsp-6 and compromises the ability of animals to cope with mitochondrial stress. Mitochondrial morphology and assembly of multi-subunit mitochondrial complexes of biotinylated proteins are also perturbed in ubl-5(RNAi) worms, indicating that UBL-5 also counteracts physiological levels of mitochondrial stress. Induction of mitochondrial stress promotes accumulation of GFP-tagged UBL-5 in nuclei of transgenic worms, suggesting that UBL-5 effects a nuclear step required for mounting a response to the threat of mitochondrial protein misfolding.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ClpP mediates activation of a mitochondrial unfolded protein response in C. elegans.Dev Cell. 2007 Oct;13(4):467-80. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.07.016. Dev Cell. 2007. PMID: 17925224
-
Compartment-specific perturbation of protein handling activates genes encoding mitochondrial chaperones.J Cell Sci. 2004 Aug 15;117(Pt 18):4055-66. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01275. Epub 2004 Jul 27. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15280428
-
The matrix peptide exporter HAF-1 signals a mitochondrial UPR by activating the transcription factor ZC376.7 in C. elegans.Mol Cell. 2010 Feb 26;37(4):529-40. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.01.015. Mol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20188671 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling the mitochondrial unfolded protein response.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Feb;1833(2):410-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.02.019. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22445420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mitochondrial UPR - protecting organelle protein homeostasis.J Cell Sci. 2010 Nov 15;123(Pt 22):3849-55. doi: 10.1242/jcs.075119. J Cell Sci. 2010. PMID: 21048161 Review.
Cited by
-
A germline-to-soma signal triggers an age-related decline of mitochondrial stress response.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 8;15(1):8723. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53064-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39379393 Free PMC article.
-
Novel imaging tools to study mitochondrial morphology in Caenorhabditis elegans.Life Sci Alliance. 2024 Sep 11;7(11):e202402918. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202402918. Print 2024 Nov. Life Sci Alliance. 2024. PMID: 39260886 Free PMC article.
-
Neuro-intestinal acetylcholine signalling regulates the mitochondrial stress response in Caenorhabditis elegans.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 3;15(1):6594. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50973-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39097618 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial inorganic polyphosphate is required to maintain proteostasis within the organelle.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jul 10;12:1423208. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1423208. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39050895 Free PMC article.
-
The Caenorhabditis elegans proteome response to two protective Pseudomonas symbionts.mBio. 2024 Apr 10;15(4):e0346323. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03463-23. Epub 2024 Feb 27. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38411078 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Artal-Sanz, M., W. Y. Tsang, E. M. Willems, L. A. Grivell, B. D. Lemire et al., 2003. The mitochondrial prohibitin complex is essential for embryonic viability and germline function in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 32091–32099. - PubMed
-
- Beal, M. F., 2005. Mitochondria take center stage in aging and neurodegeneration. Ann. Neurol. 58: 495–505. - PubMed
-
- Biaszczak, A., C. Georgopoulos and K. Liberek, 1999. On the mechanism of FtsH-dependent degradation of the sigma 32 transcriptional regulator of Escherichia coli and the role of the Dnak chaperone machine. Mol. Microbiol. 31: 157–166. - PubMed
-
- Bukau, B., 1993. Regulation of the Escherichia coli heat-shock response. Mol. Microbiol. 9: 671–680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

