Long-term depression at the mossy fiber-deep cerebellar nucleus synapse
- PMID: 16807323
- PMCID: PMC6673927
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0784-06.2006
Long-term depression at the mossy fiber-deep cerebellar nucleus synapse
Abstract
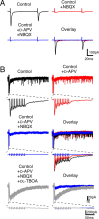
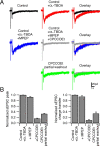
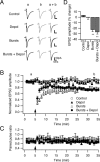
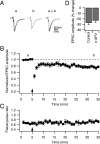
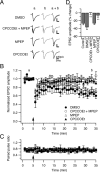
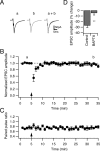
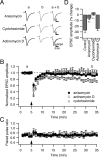
Several lines of evidence have indicated that the deep cerebellar nuclei (DCN) are a site of memory storage for certain forms of motor learning, most notably associative eyelid conditioning. In particular, these experiments, together with network models, have implicated the excitatory glutamatergic synapse between mossy fibers and DCN neurons in this memory trace. However, to date, evidence for persistent use-dependent change in the strength of this synapse has been almost entirely absent. Here, we report that high-frequency burst stimulation of mossy fibers, either alone or paired with postsynaptic depolarization, gives rise to long-term depression (LTD) of the mossy fiber-DCN synapse. This form of LTD is not associated with changes in the paired-pulse ratio and is blocked by loading with a postsynaptic Ca2+ chelator but not by bath application of an NMDA receptor antagonist. Mossy fiber-DCN LTD requires activation of a group I metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR) and protein translation. Unlike mGluR/translation-dependent LTD in other brain regions, this form of LTD requires mGluR1 and is mGluR5 independent.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulatory effects of serotonin on glutamatergic synaptic transmission and long-term depression in the deep cerebellar nuclei.Neuroscience. 2011 Jan 13;172:118-28. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.10.037. Epub 2010 Oct 20. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 20969929
-
Depolarization-induced long-term depression at hippocampal mossy fiber-CA3 pyramidal neuron synapses.J Neurosci. 2003 Oct 29;23(30):9786-95. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-30-09786.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14586006 Free PMC article.
-
Two Loci of expression for long-term depression at hippocampal mossy fiber-interneuron synapses.J Neurosci. 2004 Mar 3;24(9):2112-21. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4645-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 14999062 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacology of the metabotropic glutamate receptor mediated current at the climbing fiber to Purkinje cell synapse.Prog Brain Res. 2005;148:299-306. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(04)48023-6. Prog Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 15661198 Review.
-
GABA-ergic transmission in deep cerebellar nuclei.Prog Neurobiol. 1997 Oct;53(2):259-71. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(97)00033-6. Prog Neurobiol. 1997. PMID: 9364613 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term depression at parallel fiber to Golgi cell synapses.J Neurophysiol. 2010 Dec;104(6):3413-23. doi: 10.1152/jn.00030.2010. Epub 2010 Sep 22. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20861429 Free PMC article.
-
Distributed Circuit Plasticity: New Clues for the Cerebellar Mechanisms of Learning.Cerebellum. 2016 Apr;15(2):139-51. doi: 10.1007/s12311-015-0711-7. Cerebellum. 2016. PMID: 26304953 Review.
-
Cerebellar cortex and cerebellar nuclei are concomitantly activated during eyeblink conditioning: a 7T fMRI study in humans.J Neurosci. 2015 Jan 21;35(3):1228-39. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2492-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25609637 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of variable synaptic weights for rate and temporal coding of cerebellar outputs.Elife. 2024 Jan 19;13:e89095. doi: 10.7554/eLife.89095. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38241596 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic inhibition, excitation, and plasticity in neurons of the cerebellar nuclei.Cerebellum. 2010 Mar;9(1):56-66. doi: 10.1007/s12311-009-0140-6. Cerebellum. 2010. PMID: 19847585 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aizenman CD, Linden DJ (2000). Rapid, synaptically driven increases in the intrinsic excitability of cerebellar deep nuclear neurons. Nat Neurosci 3:109–111. - PubMed
-
- Aizenman CD, Manis PB, Linden DJ (1998). Polarity of long-term synaptic gain change is related to postsynaptic spike firing at a cerebellar inhibitory synapse. Neuron 21:827–835. - PubMed
-
- Aizenman CD, Huang EJ, Linden DJ (2003). Morphological correlates of intrinsic electrical excitability in neurons of the deep cerebellar nuclei. J Neurophysiol 89:1738–1747. - PubMed
-
- Akazawa C, Shigemoto R, Bessho Y, Nakanishi S, Mizuno N (1994). Differential expression of five N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit mRNAs in the cerebellum of developing and adult rats. J Comp Neurol 347:150–160. - PubMed
-
- Anchisi D, Scelfo B, Tempia F (2001). Postsynaptic currents in deep cerebellar nuclei. J Neurophysiol 85:323–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
