Recombinant adeno-associated virus expressing the receptor-binding domain of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus S protein elicits neutralizing antibodies: Implication for developing SARS vaccines
- PMID: 16793110
- PMCID: PMC7111904
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.03.049
Recombinant adeno-associated virus expressing the receptor-binding domain of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus S protein elicits neutralizing antibodies: Implication for developing SARS vaccines
Abstract
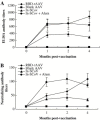
Development of an effective vaccine for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) remains to be a priority to prevent possible re-emergence of SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV). We previously demonstrated that the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of SARS-CoV S protein is a major target of neutralizing antibodies. This suggests that the RBD may serve as an ideal vaccine candidate. Recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) has been proven to be an effective system for gene delivery and vaccine development. In this study, a novel vaccine against SARS-CoV was developed based on the rAAV delivery system. The gene encoding RBD was cloned into a pAAV-IRES-hrGFP plasmid. The immunogenicity induced by the resulting recombinant RBD-rAAV was evaluated in BALB/c mice. The results demonstrated that (1) a single dose of RBD-rAAV vaccination could induce sufficient neutralizing antibody against SARS-CoV infection; (2) two more repeated doses of the vaccination boosted the neutralizing antibody to about 5 times of the level achieved by a single dose of the immunization and (3) the level of the antibody continued to increase for the entire duration of the experiment of 5.5 months. These results suggested that RBD-rAAV is a promising SARS candidate vaccine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Priming with rAAV encoding RBD of SARS-CoV S protein and boosting with RBD-specific peptides for T cell epitopes elevated humoral and cellular immune responses against SARS-CoV infection.Vaccine. 2008 Mar 20;26(13):1644-51. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.01.025. Epub 2008 Feb 4. Vaccine. 2008. PMID: 18289745 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal vaccination of recombinant adeno-associated virus encoding receptor-binding domain of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) spike protein induces strong mucosal immune responses and provides long-term protection against SARS-CoV infection.J Immunol. 2008 Jan 15;180(2):948-56. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.2.948. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18178835 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV spike protein induces long-term protective immunity in an animal model.Vaccine. 2007 Apr 12;25(15):2832-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.10.031. Epub 2006 Oct 30. Vaccine. 2007. PMID: 17092615 Free PMC article.
-
Studies of SARS virus vaccines.Hong Kong Med J. 2008 Aug;14 Suppl 4:39-43. Hong Kong Med J. 2008. PMID: 18708674 Review.
-
Vaccine design for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus.Viral Immunol. 2005;18(2):327-32. doi: 10.1089/vim.2005.18.327. Viral Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16035944 Review.
Cited by
-
Potent immunogenicity and neutralization of recombinant adeno-associated virus expressing the glycoprotein of severe fever with thrombocytopenia virus.J Vet Med Sci. 2024 Feb 15;86(2):228-238. doi: 10.1292/jvms.23-0375. Epub 2023 Dec 22. J Vet Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38143087 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of Hepatitis E Virus Anti-ORF3 Antibodies from Systemic Administration of a Muscle-Specific Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Vector.Viruses. 2022 Jan 27;14(2):266. doi: 10.3390/v14020266. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215859 Free PMC article.
-
An AAV vaccine targeting the RBD of the SARS-CoV-2 S protein induces effective neutralizing antibody titers in mice and canines.Vaccine. 2022 Feb 23;40(9):1208-1212. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2022.01.030. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Vaccine. 2022. PMID: 35094871 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on SARS-CoV-2-Induced Neuroinflammation, Neurodevelopmental Complications, and Recent Updates on the Vaccine Development.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Sep;58(9):4535-4563. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02399-6. Epub 2021 Jun 5. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34089508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vectored Immunotherapeutics for Infectious Diseases: Can rAAVs Be The Game Changers for Fighting Transmissible Pathogens?Front Immunol. 2021 May 11;12:673699. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.673699. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34046041 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anand K., Ziebuhr J., Wadhwani P., Mesters J.R., Hilgenfeld R. Coronavirus main proteinase (3CLpro) structure: basis for design of anti-SARS drugs. Science. 2003;300:1763–1767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

