LMP1 strain variants: biological and molecular properties
- PMID: 16775333
- PMCID: PMC1488979
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00135-06
LMP1 strain variants: biological and molecular properties
Abstract
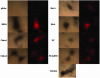
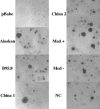
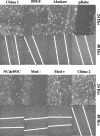
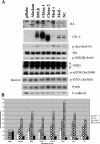
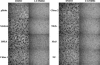
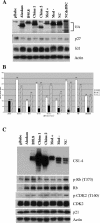
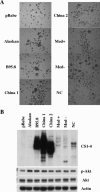
The ubiquitous herpesvirus Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is linked to the development of several malignancies, including nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) is considered the EBV oncogene as it is necessary for EBV-induced transformation of B lymphocytes and is able to transform Rat-1 fibroblasts. LMP1 can activate a wide array of signaling pathways, including phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt and NF-kappaB. Six sequence variants of LMP1, termed Alaskan, China 1, China 2, Med+, Med-, and NC, have been identified, and individuals can be infected with multiple variants. The frequencies of detection of these variants differ for various EBV-associated malignancies from different geographic regions. In this study, the biological and signaling properties of the LMP1 variants have been characterized. All of the LMP1 variants transformed Rat-1 fibroblasts, induced increased motility of HFK cells, and induced increased homotypic adhesion of BJAB cells. While all the variants activated the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway to similar extents, the Alaskan, China 1, and Med+ variants had limited binding to the E3 ubiquitin ligase component homologue of Slimb and had slightly enhanced NF-kappaB signaling. These findings indicate that the signature amino acid changes of the LMP1 variants do not hinder or enhance their in vitro transforming potentials or affect their signaling properties.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Unique signaling properties of CTAR1 in LMP1-mediated transformation.J Virol. 2007 Sep;81(18):9680-92. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01001-07. Epub 2007 Jul 11. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17626074 Free PMC article.
-
Positive regulation of HIF-1A expression by EBV oncoprotein LMP1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.Cancer Lett. 2016 Nov 1;382(1):21-31. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.08.021. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 27567526
-
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein 1 induces interleukin-8 through the nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway in EBV-infected nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line.Laryngoscope. 2004 May;114(5):855-9. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200405000-00012. Laryngoscope. 2004. PMID: 15126743
-
The Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1).Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:119-49. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_4. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428373 Review.
-
Novel roles and therapeutic targets of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1-induced oncogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2015 Aug 18;17:e15. doi: 10.1017/erm.2015.13. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26282825 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of DNA Damage Signaling and Cell Death Responses by Epstein-Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1) and LMP2A in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells.J Virol. 2015 Aug;89(15):7612-24. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00958-15. Epub 2015 May 13. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25972552 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and Characterization of an Epstein-Barr Virus-positive Cell Line from a Non-keratinizing Differentiated Primary Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Cancer Res Commun. 2024 Mar 4;4(3):645-659. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-23-0341. Cancer Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38358347 Free PMC article.
-
Using Epstein-Barr viral load assays to diagnose, monitor, and prevent posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010 Apr;23(2):350-66. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00006-09. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20375356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional downregulation of p27KIP1 through regulation of E2F function during LMP1-mediated transformation.J Virol. 2009 Dec;83(24):12671-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01422-09. Epub 2009 Oct 14. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19828622 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of SPLUNC1 protein on the Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Epstein-Barr virus.Mol Cell Biochem. 2008 Feb;309(1-2):191-7. doi: 10.1007/s11010-007-9659-3. Epub 2007 Nov 30. Mol Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 18049866
References
-
- Arvanitakis, L., N. Yaseen, and S. Sharma. 1995. Latent membrane protein-1 induces cyclin D2 expression, pRb hyperphosphorylation, and loss of TGF-beta 1-mediated growth inhibition in EBV-positive B cells. J. Immunol. 155:1047-1056. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson, P. G., H. J. Coope, M. Rowe, and S. C. Ley. 2003. Latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein-Barr virus stimulates processing of NF-kappa B2 p100 to p52. J. Biol. Chem. 278:51134-51142. - PubMed
-
- Babcock, G. J., L. L. Decker, M. Volk, and D. A. Thorley-Lawson. 1998. EBV persistence in memory B cells in vivo. Immunity 9:395-404. - PubMed
-
- Blake, S. M., A. G. Eliopoulos, C. W. Dawson, and L. S. Young. 2001. The transmembrane domains of the EBV-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) variant CAO regulate enhanced signalling activity. Virology 282:278-287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

