CaM kinase II selectively signals to histone deacetylase 4 during cardiomyocyte hypertrophy
- PMID: 16767219
- PMCID: PMC1474817
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI27438
CaM kinase II selectively signals to histone deacetylase 4 during cardiomyocyte hypertrophy
Abstract
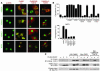
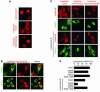
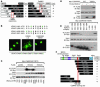
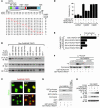
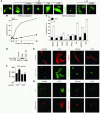
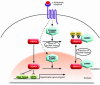
Class IIa histone deacetylases (HDACs) regulate a variety of cellular processes, including cardiac growth, bone development, and specification of skeletal muscle fiber type. Multiple serine/threonine kinases control the subcellular localization of these HDACs by phosphorylation of common serine residues, but whether certain class IIa HDACs respond selectively to specific kinases has not been determined. Here we show that calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII) signals specifically to HDAC4 by binding to a unique docking site that is absent in other class IIa HDACs. Phosphorylation of HDAC4 by CaMKII promotes nuclear export and prevents nuclear import of HDAC4, with consequent derepression of HDAC target genes. In cardiomyocytes, CaMKII phosphorylation of HDAC4 results in hypertrophic growth, which can be blocked by a signal-resistant HDAC4 mutant. These findings reveal a central role for HDAC4 in CaMKII signaling pathways and have implications for the control of gene expression by calcium signaling in a variety of cell types.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Class II HDACs mediate CaMK-dependent signaling to NRSF in ventricular myocytes.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2006 Dec;41(6):1010-22. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2006.08.010. Epub 2006 Oct 2. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2006. PMID: 17011572
-
14-3-3 regulates the nuclear import of class IIa histone deacetylases.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Dec 19;377(3):852-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.10.079. Epub 2008 Oct 24. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. PMID: 18952052
-
New role for hPar-1 kinases EMK and C-TAK1 in regulating localization and activity of class IIa histone deacetylases.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Oct;26(19):7086-102. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00231-06. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16980613 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory signal transduction pathways for class IIa histone deacetylases.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010 Aug;10(4):454-60. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2010.04.004. Epub 2010 May 4. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20447866 Review.
-
Class II histone deacetylases: structure, function, and regulation.Biochem Cell Biol. 2001;79(3):243-52. Biochem Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11467738 Review.
Cited by
-
Exercise adaptations: molecular mechanisms and potential targets for therapeutic benefit.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020 Sep;16(9):495-505. doi: 10.1038/s41574-020-0377-1. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32632275 Review.
-
Nutraceutical, Dietary, and Lifestyle Options for Prevention and Treatment of Ventricular Hypertrophy and Heart Failure.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 24;22(7):3321. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073321. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33805039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The steroid hormone 20-hydroxyecdysone via nongenomic pathway activates Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II to regulate gene expression.J Biol Chem. 2015 Mar 27;290(13):8469-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.622696. Epub 2015 Feb 10. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25670853 Free PMC article.
-
miR-378a-3p promotes differentiation and inhibits proliferation of myoblasts by targeting HDAC4 in skeletal muscle development.RNA Biol. 2016 Dec;13(12):1300-1309. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1239008. Epub 2016 Sep 23. RNA Biol. 2016. PMID: 27661135 Free PMC article.
-
Role of endothelin in the induction of cardiac hypertrophy in vitro.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43179. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043179. Epub 2012 Aug 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22912821 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roth S.Y., Denu J.M., Allis C.D. Histone acetyltransferases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001;70:81–120. - PubMed
-
- Grozinger C.M., Schreiber S.L. Deacetylase enzymes: biological functions and the use of small-molecule inhibitors. Chem. Biol. 2002;9:3–16. - PubMed
-
- Backs J., Olson E.N. Control of cardiac growth by histone acetylation/deacetylation. Circ. Res. 2006;98:15–24. - PubMed
-
- Verdin E., Dequiedt F., Kasler H.G. Class II histone deacetylases: versatile regulators. Trends Genet. 2003;19:286–293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

