A dynein loading zone for retrograde endosome motility at microtubule plus-ends
- PMID: 16688221
- PMCID: PMC1478194
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601119
A dynein loading zone for retrograde endosome motility at microtubule plus-ends
Abstract
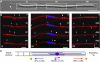
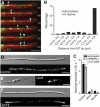
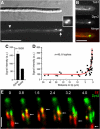
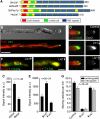
In the fungus Ustilago maydis, early endosomes move bidirectionally along microtubules (MTs) and facilitate growth by local membrane recycling at the tip of the infectious hypha. Here, we set out to elucidate the molecular mechanism of this process. We show that endosomes travel by Kinesin-3 activity into the hyphal apex, where they reverse direction and move backwards in a dynein-dependent manner. Our data demonstrate that dynein, dynactin and Lis1 accumulate at MT plus-ends within the hyphal tip, where they provide a reservoir of inactive motors for retrograde endosome transport. Consistently, endosome traffic is abolished after depletion of the dynein activator Lis1 and in Kinesin-1 null mutants, which was due to a defect in targeting of dynein and dynactin to the apical MT plus-ends. Furthermore, biologically active GFP-dynein travels on endosomes in retrograde and not in anterograde direction. Surprisingly, a CLIP170 homologue was neither needed for dynein localization nor for endosome transport. These results suggest an apical dynein loading zone in the hyphal tip, which ensure that endosomes reach the expanding growth region before they reverse direction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A balance of KIF1A-like kinesin and dynein organizes early endosomes in the fungus Ustilago maydis.EMBO J. 2002 Jun 17;21(12):2946-57. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf296. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 12065408 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of a vezatin-like protein for dynein-mediated early endosome transport.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Nov 1;26(21):3816-27. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-08-0602. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 26378255 Free PMC article.
-
The microtubule plus-end localization of Aspergillus dynein is important for dynein-early-endosome interaction but not for dynein ATPase activation.J Cell Sci. 2010 Oct 15;123(Pt 20):3596-604. doi: 10.1242/jcs.075259. Epub 2010 Sep 28. J Cell Sci. 2010. PMID: 20876661 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic dynein and early endosome transport.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Sep;72(17):3267-80. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1926-y. Epub 2015 May 23. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26001903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tracks for traffic: microtubules in the plant pathogen Ustilago maydis.New Phytol. 2007;174(4):721-733. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02072.x. New Phytol. 2007. PMID: 17504456 Review.
Cited by
-
DBZ regulates cortical cell positioning and neurite development by sustaining the anterograde transport of Lis1 and DISC1 through control of Ndel1 dual-phosphorylation.J Neurosci. 2015 Feb 18;35(7):2942-58. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5029-13.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25698733 Free PMC article.
-
Endosomal maturation by Rab conversion in Aspergillus nidulans is coupled to dynein-mediated basipetal movement.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 May;23(10):1889-901. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-11-0925. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22456509 Free PMC article.
-
LIS1 regulates cargo-adapter-mediated activation of dynein by overcoming its autoinhibition in vivo.J Cell Biol. 2019 Nov 4;218(11):3630-3646. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201905178. Epub 2019 Sep 27. J Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31562232 Free PMC article.
-
The fungus Ustilago maydis and humans share disease-related proteins that are not found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.BMC Genomics. 2007 Dec 20;8:473. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-473. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 18096044 Free PMC article.
-
The actin capping protein in Aspergillus nidulans enhances dynein function without significantly affecting Arp1 filament assembly.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 30;8(1):11419. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29818-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30061726 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bottin A, Kamper J, Kahmann R (1996) Isolation of a carbon source-regulated gene from Ustilago maydis. Mol Gen Genet 253: 342–352 - PubMed
-
- Brachmann A, Weinzierl G, Kamper J, Kahmann R (2001) Identification of genes in the bW/bE regulatory cascade in Ustilago maydis. Mol Microbiol 42: 1047–1063 - PubMed
-
- Brunner D, Nurse P (2000) CLIP170-like tip1p spatially organizes microtubular dynamics in fission yeast. Cell 102: 695–704 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

