Dynamic regulation of caveolin-1 trafficking in the germ line and embryo of Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 16672374
- PMCID: PMC1483042
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e06-03-0211
Dynamic regulation of caveolin-1 trafficking in the germ line and embryo of Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
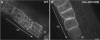
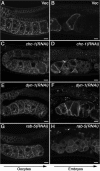
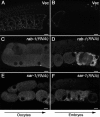
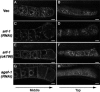
Caveolin is the major protein component required for the formation of caveolae on the plasma membrane. Here we show that trafficking of Caenorhabditis elegans caveolin-1 (CAV-1) is dynamically regulated during development of the germ line and embryo. In oocytes a CAV-1-green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion protein is found on the plasma membrane and in large vesicles (CAV-1 bodies). After ovulation and fertilization the CAV-1 bodies fuse with the plasma membrane in a manner reminiscent of cortical granule exocytosis as described in other species. Fusion of CAV-1 bodies with the plasma membrane appears to be regulated by the advancing cell cycle, and not fertilization per se, because fusion can proceed in spe-9 fertilization mutants but is blocked by RNA interference-mediated knockdown of an anaphase-promoting complex component (EMB-27). After exocytosis, most CAV-1-GFP is rapidly endocytosed and degraded within one cell cycle. CAV-1 bodies in oocytes appear to be produced by the Golgi apparatus in an ARF-1-dependent, clathrin-independent, mechanism. Conversely endocytosis and degradation of CAV-1-GFP in embryos requires clathrin, dynamin, and RAB-5. Our results demonstrate that the distribution of CAV-1 is highly dynamic during development and provides new insights into the sorting mechanisms that regulate CAV-1 localization.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rab11 is required for synchronous secretion of chondroitin proteoglycans after fertilization in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Cell Sci. 2008 Oct 1;121(Pt 19):3177-86. doi: 10.1242/jcs.034678. Epub 2008 Sep 2. J Cell Sci. 2008. PMID: 18765566
-
Rab6 is required for the exocytosis of cortical granules and the recruitment of separase to the granules during the oocyte-to-embryo transition in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Cell Sci. 2012 Dec 1;125(Pt 23):5897-905. doi: 10.1242/jcs.116400. Epub 2012 Sep 19. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22992455
-
Caveolin-2 is required for apical lipid trafficking and suppresses basolateral recycling defects in the intestine of Caenorhabditis elegans.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Mar;20(6):1763-71. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-08-0837. Epub 2009 Jan 21. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19158391 Free PMC article.
-
[C. elegans, an amenable model system for the study of membrane trafficking in living animals].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2008 Dec;53(16 Suppl):2188-92. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2008. PMID: 21038606 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Dynamic regulation of autophagy and endocytosis for cell remodeling during early development.Traffic. 2013 May;14(5):479-86. doi: 10.1111/tra.12050. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Traffic. 2013. PMID: 23356349 Review.
Cited by
-
MARC-3, a membrane-associated ubiquitin ligase, is required for fast polyspermy block in Caenorhabditis elegans.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 26;15(1):792. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44928-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38278786 Free PMC article.
-
Reorganization, specialization, and degradation of oocyte maternal components for early development.Reprod Med Biol. 2023 Jan 28;22(1):e12505. doi: 10.1002/rmb2.12505. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Reprod Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 36726596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-translational regulation of the maternal-to-zygotic transition.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018 May;75(10):1707-1722. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2750-y. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29427077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An RNAi-based suppressor screen identifies interactors of the Myt1 ortholog of Caenorhabditis elegans.G3 (Bethesda). 2014 Oct 8;4(12):2329-43. doi: 10.1534/g3.114.013649. G3 (Bethesda). 2014. PMID: 25298536 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol depletion disorganizes oocyte membrane rafts altering mouse fertilization.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 25;8(4):e62919. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062919. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23638166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott A. L., Ducibella T. Calcium and the control of mammalian cortical granule exocytosis. Front Biosci. 2001;6:D792–D806. - PubMed
-
- Anderson R. G. The caveolae membrane system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998;67:199–225. - PubMed
-
- Bonifacino J. S. The GGA proteins: adaptors on the move. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004;5:23–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

