p21Cip1 is required for the development of monocytes and their response to serum transfer-induced arthritis
- PMID: 16651620
- PMCID: PMC1606593
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050555
p21Cip1 is required for the development of monocytes and their response to serum transfer-induced arthritis
Abstract
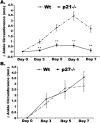
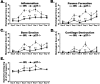
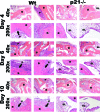
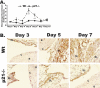
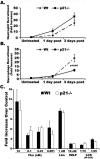
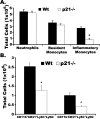
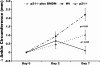
One of the central functions of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, such as p21, p27, or p16, is to prevent entry into the cell cycle. However, the question remains as to whether they have other functions in the cell. We previously demonstrated that overexpression of p21 in fibroblasts isolated from patients with rheumatoid arthritis decreases the production of pro-inflammatory molecules. Overexpression of p21 has been also shown to reduce the development of experimental arthritis in mice and rats. To explore the role of endogenous p21 in the development of arthritis, we induced arthritis in p21(-/-) mice using the K/BxN serum transfer model of arthritis. Mice deficient in p21 were more resistant to serum transfer-induced arthritis (K/BxN) than wild-type (wt) control mice. Fewer macrophages were detected in p21(-/-) as compared to wt joints following transfer of K/BxN serum. Chemotaxis assays of bone marrow-derived macrophages from p21(-/-) and wt mice revealed no difference in migration. However, there was a substantial decrease in inflammatory monocytes circulating in peripheral blood and in monocyte precursors in bone marrow of p21(-/-) mice as compared to wt mice. Adoptive transfer of wt bone marrow-derived macrophages into p21(-/-) mice restored the sensitivity to serum transfer-induced arthritis. These data suggest a novel role for p21 in regulating the development and/or differentiation of monocytic populations that are crucial for the induction of inflammatory arthritis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21, via its C-terminal domain, is essential for resolution of murine inflammatory arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Jan;64(1):141-52. doi: 10.1002/art.33311. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 21898359 Free PMC article.
-
Kruppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) regulates monocyte differentiation and functions in mBSA and IL-1β-induced arthritis.Curr Mol Med. 2012 Feb;12(2):113-25. doi: 10.2174/156652412798889090. Curr Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22280353 Free PMC article.
-
Adenoviral transfer of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor genes suppresses collagen-induced arthritis in mice.J Immunol. 2000 Dec 15;165(12):7246-52. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.12.7246. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11120858
-
RANKL coordinates cell cycle withdrawal and differentiation in osteoclasts through the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p27KIP1 and p21CIP1.J Bone Miner Res. 2004 Aug;19(8):1339-48. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.040321. Epub 2004 Mar 29. J Bone Miner Res. 2004. PMID: 15231022
-
Studying Neutrophil Migration In Vivo Using Adoptive Cell Transfer.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1407:179-94. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3480-5_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27271903
Cited by
-
TLR2 deletion promotes arthritis through reduction of IL-10.J Leukoc Biol. 2013 May;93(5):751-9. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0912473. Epub 2013 Feb 27. J Leukoc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23446149 Free PMC article.
-
Stromal and therapy-induced macrophage proliferation promotes PDAC progression and susceptibility to innate immunotherapy.J Exp Med. 2023 Jun 5;220(6):e20212062. doi: 10.1084/jem.20212062. Epub 2023 Mar 23. J Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36951731 Free PMC article.
-
NUR who? An orphan transcription factor holds promise for monomaniacs.Nat Immunol. 2011 Jul 19;12(8):727-9. doi: 10.1038/ni.2074. Nat Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21772283 No abstract available.
-
Antibody-induced arthritis: disease mechanisms and genes involved at the effector phase of arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(6):223. doi: 10.1186/ar2089. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006. PMID: 17254316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Increased F4/80high Macrophages With Suppression of Serum-Transfer Arthritis in Mice With Reduced FLIP in Myeloid Cells.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017 Sep;69(9):1762-1771. doi: 10.1002/art.40151. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28511285 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sherr CJ. Cancer cell cycles. Science. 1996;274:1672–1677. - PubMed
-
- Gao CY, Zelenka PS. Cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases and differentiation. BioEssays. 1997;19:307–315. - PubMed
-
- Kitaura H, Shinshi M, Uchikoshi Y, Ono T, Iguchi-Ariga SM, Ariga H. Reciprocal regulation via protein-protein interaction between c-Myc and p21(cip1/waf1/sdi1) in DNA replication and transcription. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:10477–10483. - PubMed
-
- Shim J, Lee H, Park J, Kim H, Choi EJ. A non-enzymatic p21 protein inhibitor of stress-activated protein kinases. Nature. 1996;381:804–806. - PubMed
-
- Coqueret O, Gascan H. Functional interaction of STAT3 transcription factor with the cell cycle inhibitor p21WAF1/CIP1/SDI1. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:18794–18800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

