Molecular diversity of coronaviruses in bats
- PMID: 16647731
- PMCID: PMC7111821
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.02.041
Molecular diversity of coronaviruses in bats
Abstract
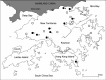
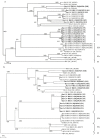
The existence of coronaviruses in bats is unknown until the recent discovery of bat-SARS-CoV in Chinese horseshoe bats and a novel group 1 coronavirus in other bat species. Among 309 bats of 13 species captured from 20 different locations in rural areas of Hong Kong over a 16-month period, coronaviruses were amplified from anal swabs of 37 (12%) bats by RT-PCR. Phylogenetic analysis of RNA-dependent-RNA-polymerase (pol) and helicase genes revealed six novel coronaviruses from six different bat species, in addition to the two previously described coronaviruses. Among the six novel coronaviruses, four were group 1 coronaviruses (bat-CoV HKU2 from Chinese horseshoe bat, bat-CoV HKU6 from rickett's big-footed bat, bat-CoV HKU7 from greater bent-winged bat and bat-CoV HKU8 from lesser bent-winged bat) and two were group 2 coronaviruses (bat-CoV HKU4 from lesser bamboo bats and bat-CoV HKU5 from Japanese pipistrelles). An astonishing diversity of coronaviruses was observed in bats.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic characterization of Betacoronavirus lineage C viruses in bats reveals marked sequence divergence in the spike protein of pipistrellus bat coronavirus HKU5 in Japanese pipistrelle: implications for the origin of the novel Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus.J Virol. 2013 Aug;87(15):8638-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01055-13. Epub 2013 May 29. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23720729 Free PMC article.
-
Complete genome sequence of bat coronavirus HKU2 from Chinese horseshoe bats revealed a much smaller spike gene with a different evolutionary lineage from the rest of the genome.Virology. 2007 Oct 25;367(2):428-39. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.06.009. Epub 2007 Jul 6. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17617433 Free PMC article.
-
Coronaviruses in bent-winged bats (Miniopterus spp.).J Gen Virol. 2006 Sep;87(Pt 9):2461-2466. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.82203-0. J Gen Virol. 2006. PMID: 16894183
-
Bat origin of human coronaviruses.Virol J. 2015 Dec 22;12:221. doi: 10.1186/s12985-015-0422-1. Virol J. 2015. PMID: 26689940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronavirus diversity, phylogeny and interspecies jumping.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2009 Oct;234(10):1117-27. doi: 10.3181/0903-MR-94. Epub 2009 Jun 22. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2009. PMID: 19546349 Review.
Cited by
-
A real-time PCR assay for bat SARS-like coronavirus detection and its application to Italian greater horseshoe bat faecal sample surveys.ScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012:989514. doi: 10.1100/2012/989514. Epub 2011 Nov 22. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012. PMID: 22654650 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of coronavirus in bats from Eastern Thailand.Virol J. 2015 Apr 11;12:57. doi: 10.1186/s12985-015-0289-1. Virol J. 2015. PMID: 25884446 Free PMC article.
-
Ecoepidemiology and complete genome comparison of different strains of severe acute respiratory syndrome-related Rhinolophus bat coronavirus in China reveal bats as a reservoir for acute, self-limiting infection that allows recombination events.J Virol. 2010 Mar;84(6):2808-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02219-09. Epub 2010 Jan 13. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20071579 Free PMC article.
-
Design and validation of consensus-degenerate hybrid oligonucleotide primers for broad and sensitive detection of corona- and toroviruses.J Virol Methods. 2011 Nov;177(2):174-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2011.08.005. Epub 2011 Aug 11. J Virol Methods. 2011. PMID: 21864579 Free PMC article.
-
The taxonomy, host range and pathogenicity of coronaviruses and other viruses in the Nidovirales order.Anim Dis. 2021;1(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s44149-021-00005-9. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Anim Dis. 2021. PMID: 34778878 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Eickmann M., Becker S., Klenk H.D., Doerr H.W., Stadler K., Censini S., Guidotti S., Masignani V., Scarselli M., Mora M., Donati C., Han J.H., Song H.C., Abrignani S., Covacci A., Rappuoli R. Phylogeny of the SARS coronavirus. Science. 2003;302:1504–1505. - PubMed
-
- Guan Y., Zheng B.J., He Y.Q., Liu X.L., Zhuang Z.X., Cheung C.L., Luo S.W., Li P.H., Zhang L.J., Guan Y.J., Butt K.M., Wong K.L., Chan K.W., Lim W., Shortridge K.F., Yuen K.Y., Peiris J.S., Poon L.L. Isolation and characterization of viruses related to the SARS coronavirus from animals in southern China. Science. 2003;302:276–278. - PubMed
-
- Jonassen C.M., Kofstad T., Larsen I.L., Lovland A., Handeland K., Follestad A., Lillehaug A. Molecular identification and characterization of novel coronaviruses infecting graylag geese (Anser anser), feral pigeons (Columbia livia) and mallards (Anas platyrhynchos) J. Gen. Virol. 2005;86:1597–1607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

